The first stem cell culture method that produces a full model of the early stages of the human central nervous system has been developed by a team of engineers and biologists at the University of Michigan, the Weizmann Institute of Science, and the University of Pennsylvania. The system is an example of a 3D human […]
Author Archives: Karely Vega, MD
Recombinant protein vaccines, like the Novavax vaccine used to fight COVID-19, offer several advantages over conventional vaccines. They’re easy to precisely produce. They’re safe, and potentially more effective. And they could require smaller doses. Because of these traits, there is much interest in developing recombinant influenza vaccines. To date, however, the Food and Drug Administration […]
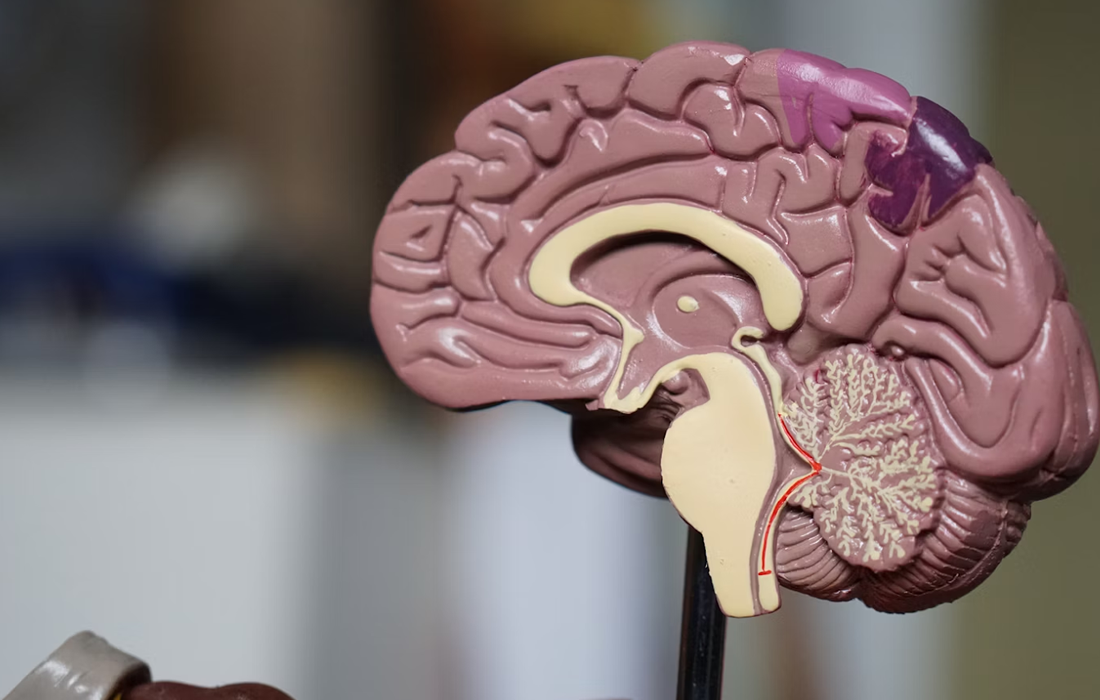
The human brain’s adaptability to internal and external changes, known as neural plasticity, forms the foundation for understanding cognitive functions like memory and learning, as well as various neurological disorders. New research conducted by a team led by Dr. PARK Joo Min of the Center for Cognition and Sociality within the Institute for Basic Science […]
A new technique for electrospinning sponges has allowed scientists from the University of Surrey to directly produce 3D scaffolds — on which skin grafts could be grown from the patient’s own skin. Electrospinning is a technique which electrifies droplets of liquid to form fibres from plastics. Previously, scientists had only been able to make 2D […]
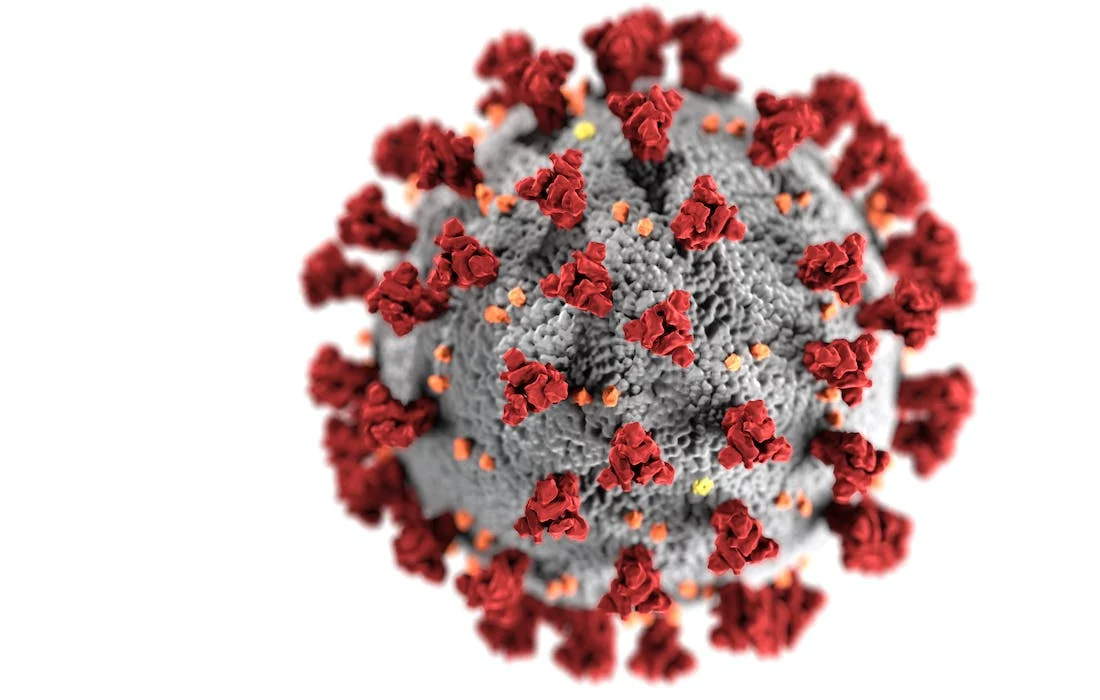
Today, a team of scientists from Trinity College Dublin and investigators from FutureNeuro announced a major discovery that has profound importance for our understanding of brain fog and cognitive decline seen in some patients with Long COVID. In the months after the emergence of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV2 in late 2019 a patient-reported syndrome termed […]
Our cells are surrounded by a fragile membrane that’s only 5 nanometers thick, 1/20 of a soap bubble. Cells are easily damaged by physiological activities, including muscle contraction and tissue injury. To cope with such damage, cells are equipped with mechanisms that can repair membrane damage to a certain degree. Mechanical damage to the cell […]
The gut microbiome interacts with the loss of female sex hormones to exacerbate metabolic disease, including weight gain, fat in the liver and the expression of genes linked with inflammation, researchers found in a new rodent study. The findings, published in the journal Gut Microbes, may shed light on why women are at significantly greater […]
In recent news, there has been a case where a patient experienced pain due to a surgical procedure involving sutures, resulting in the unintended presence of gauze within the patient’s body. Gauze is typically employed to control bleeding during medical interventions, aiding in hemostasis. However, when inadvertently left in the body, it can lead to […]
The drug finasteride, also known as Propecia or Proscar, treats male pattern baldness and enlarged prostate in millions of men worldwide. But a new University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign study suggests the drug may also provide a surprising and life-saving benefit: lowering cholesterol and cutting the overall risk of cardiovascular disease. The study, published in the […]
Injuries in the central nervous system heal poorly because cavities scar. Researchers hope to remedy this problem by filling the cavities in such a way that stem cells feel comfortable in them. The researchers studied neural stem cells from mouse embryonic brains, which they cultivated on positively charged hydrogels. “Our aim was to create an […]