Stem Cell Therapy for Specific Conditions
Can Stem Cells be Used to Treat COPD?
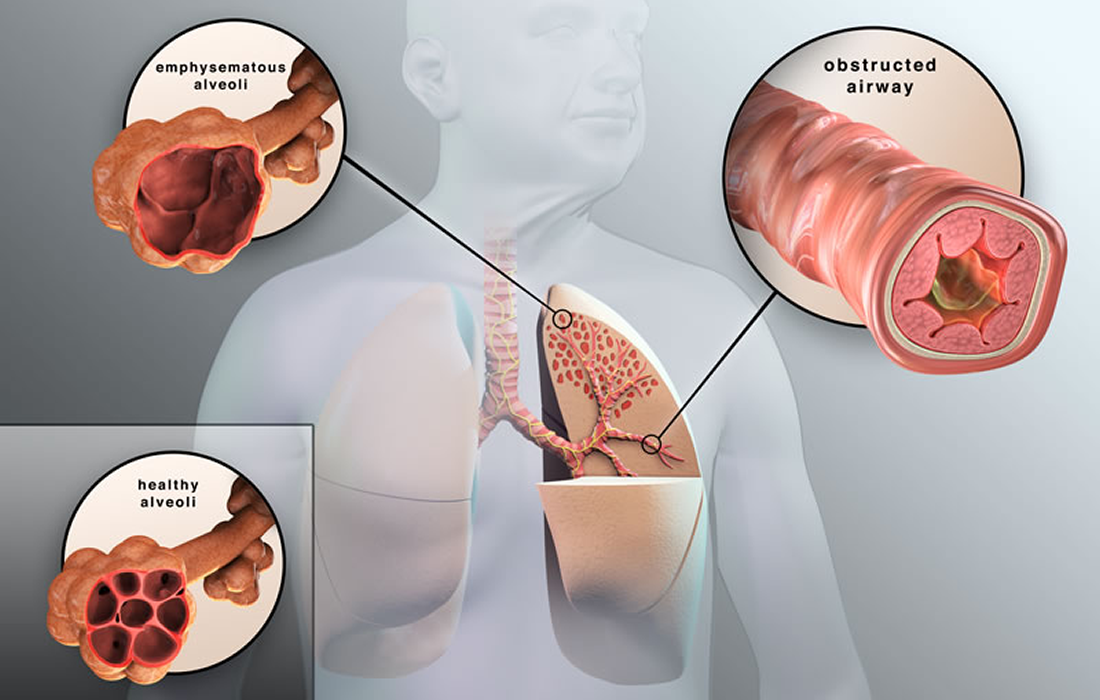
Chronic Pulmonary Obstructive Disease (COPD) is a progressive, incurable disease that affects at least 16 million people in the United States. As current treatments cannot cure COPD, many people with this condition seek alternative therapies such as stem cell therapy.
Current standard therapies including bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids and the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, roflumilast, show modest efficacy at best in reducing exacerbations and improving lung function, and there has been no definitive evidence that they impact mortality.
Stem cells can differentiate into several different lung cell types such as alveolar epithelial cells that are destroyed by cigarette smoke leading to emphysematous changes and reduced tethering of small airways causing hyperinflation and gas exchange abnormalities. Some studies performed in animal models have suggested regeneration of alveolar-like structures, repair of emphysematous lungs and reduction of inflammatory responses.
There are different types of stem cells, they can be from autologous tissues (from your own body) like bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs), adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells (AD-MSCs) and others derived from neonatal tissue, like mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly (WJ-MSCs).
Researchers think that autologous stem cell transplant in older patients may be compromised by several age-related factors including oxidative stress, telomere length, DNA damage, chronic disease and long term use of medications and that WJ-MSCs may adapt better to the host tissue environment and that they possess superior anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties.
These types of mesenchymal stem cells have unique properties that make them a favorable source for cells including factors such as their more primitive characteristics, abundant availability, noninvasive and painless collection, also they lack teratogenicity and immunogenicity compared to the other type of cells.
Stem cell therapy has shown some potential as a treatment option. According to the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the therapy has shown promise in animal studies. There are some clinical human studies ongoing that are evaluating the use of stem cells to treat COPD.
The National Emphysema Foundation points out that people who have used stem cell therapies are often willing to get further infusions, suggesting a positive experience.
The use of stem cells to treat COPD continues being evaluated due to the good results shown in animal studies and because of the lack of current curative treatments and there is no evidence that current therapies impact mortality.
Source:
Balkissoon R. Stem Cell Therapy for COPD: Where are we?. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2018;5(2):148-153. Published 2018 Jan 18.
Source link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6190524/?report=classic
Source link: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/stem-cell-therapy-for-copd#does-it-work