COVID-19
Monoclonal Antibody treatment for COVID-19
As COVID-19 cases continue to surge throughout the United States and the world, demand for monoclonal antibody treatments is spiking, especially in areas with low vaccination rates.
According to the FDA, this experimental treatment uses laboratory-made proteins that mimic the immune system’s ability to fight off harmful antigens such as viruses like SARS-CoV-2. It’s specially useful for people with weakened immune systems who may not generate a robust response to the COVID-19 vaccines, and for others at high risk of severe illness.
While monoclonal antibodies can start to clear the coronavirus within hours of being infused intravenously into the body, the treatment may not work for everyone. That’s why experts recommend that people get fully vaccinated, which is known to prevent severe illness and hospitalization due to the disease.
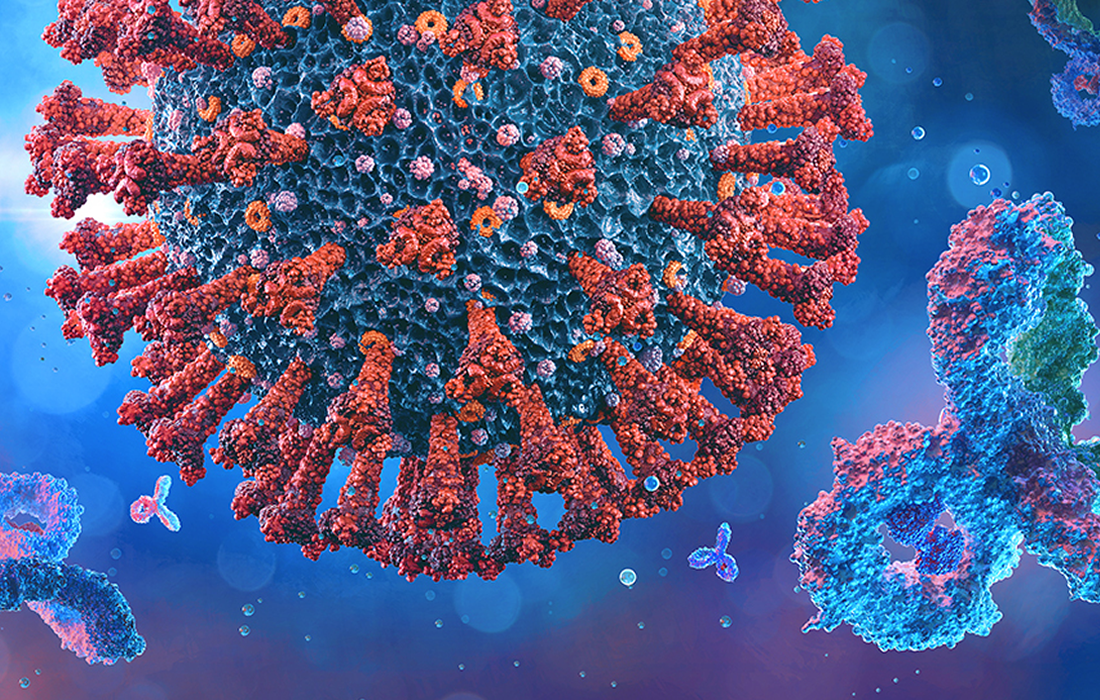
Monoclonal antibodies are a type of protein made in the laboratory that can bind to substances in the body, including cancer cells or in this case viruses. There are many kinds of monoclonal antibodies. They are made so that it binds to only one substance.
They can function like antibodies made by the immune system in response to an infection. By binding to a specific molecule on a virus or bacteria, known as antigen, a monoclonal antibody can enhance or restore the immune response against these pathogens. These type of treatments have been used and tested for other viruses like the Ebola virus and the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), as well as chronic illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Most of the monoclonal antibodies being developed to treat COVID-19 target the spike protein, which the coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) uses to enter the host cells. By binding to the spike protein, a monoclonal antibody can help prevent the virus from infecting human cells. Research suggests that certain monoclonal antibodies can reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in people with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19.
Some of the monoclonal antibodies with emergency approval from the FDA and being used:
- REGEN-COV: this drug cocktail contains 2 monoclonal antibodies, casirivimab and imbevimab. Approved for people over age 12.
- Sotrovimab: authorized for adults and kids over 12 years old.
- Tocilizumab: authorized for COVID-19 treatment in hospitalized adults and children 2 years and older. It reduces the inflammation that occurs during the infection.
Source: