Regenerative Medicine News and General Information
New Technique Could Unveil a Path Towards an HIV Cure
To develop new therapeutics and curative strategies for HIV an improved understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the virus replication, persistence and pathogenesis are critical. Studies have identified several well-characterized host factors that influence HIV replication, but attempts to identify and catalog host factors with genetic means have yielded limited results.
Now scientists at Northwestern Medicine are using new advances in CRISPR gene-editing technology to uncover new biology that could lead to the development of new treatment options and strategies to combat HIV. Their results were published in the journal Nature Communications.
New Gene-Editing Approach
The team used CRISPR gene-editing to identify human genes that were important for HIV infection in the blood, finding 86 genes that may play a role in the way HIV replicates and causes disease.
With the CRISPR system genes are either on or off. This capability to turn genes on and off in cells isolated directly from human blood is a game-changer according to Judd Hultquist, a co-corresponding author.
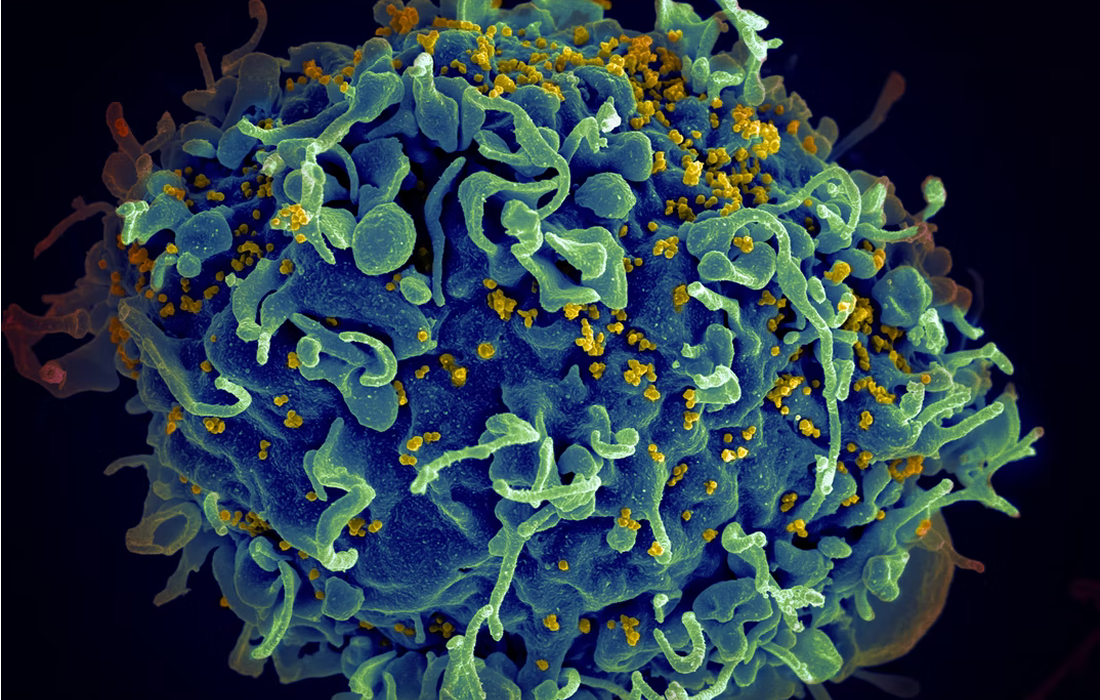
In the study, T cells, which are the major cell type targeted by the virus were isolated from donated human blood, and hundreds of genes were knocked out using CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing. Cells with knocked-out genes important for replication showed decreased infection.
The findings will potentially lead to new therapeutic strategies, which could help millions of patients that are affected every year by this virus.
Sources:
Northwestern University. “CRISPR and HIV: New technique in human blood unveils potential paths toward cure: Key to possible HIV cure may lie in mechanisms behind how it replicates.” ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 1 April 2022.
<www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/04/220401160537.htm>.
Joseph Hiatt, et al. A functional map of HIV-host interactions in primary human T cells. Nature Communications, 2022; 13 (1) DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29346-w
Image from:
Photo by National Cancer Institute on Unsplash