Stem Cell Therapy for Specific Conditions
Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
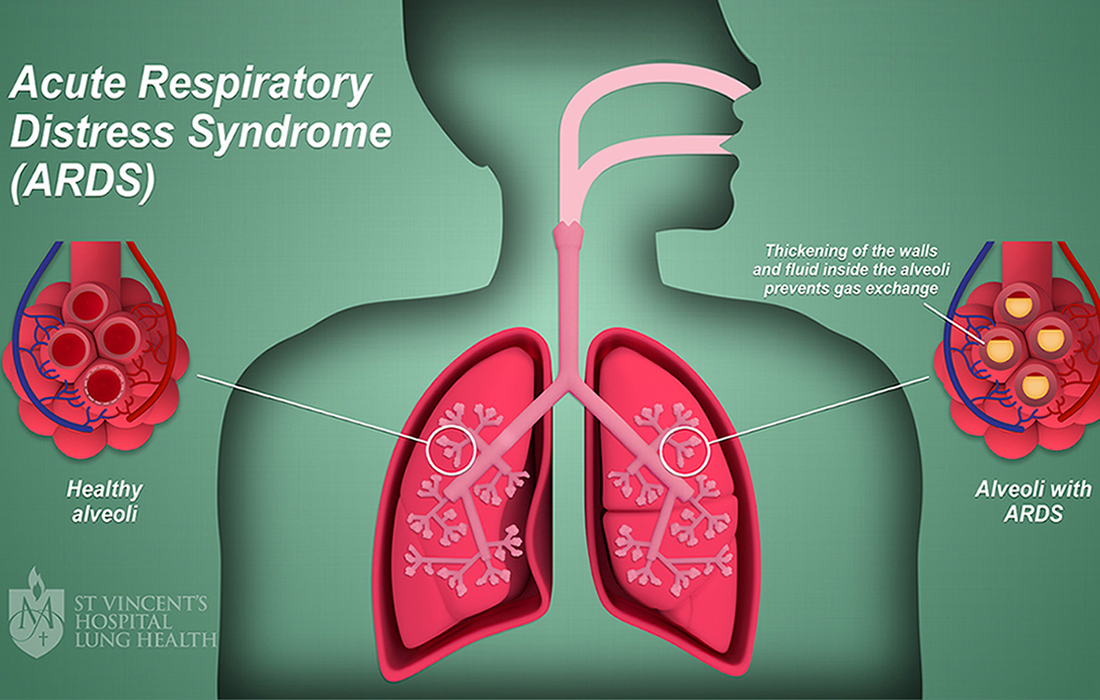
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a rapid onset of diffuse lung injury arising from a variety of insults, along with refractory hypoxemia ranging from mild to severe. It can lead to a devastating hypoxemic respiratory failure, characterized by disruption of the alveolar-capillary membrane barrier.
The current management of this condition remains supportive, and includes lung protective ventilation, prone positioning and a conservative fluid strategy. The only pharmacological interventions are mainly towards targeting the inflammatory response to reverse the course of ARDS.
The use of Mesenchymal Stem Cells is being considered as a promising intervention for treating this condition due to the ability of the cells to secrete different anti-inflammatory factors, angiogenesis, anti-fibrosis and anti-apoptosis properties.
Current studies support that the mechanism of action of MSC responsible for injured tissue repair mainly depends on their paracrine property rather than differentiation. What this means is that the MSC secrete different factors that cause an action on a different cell. They can cause an increase in clearance of alveolar fluid, regulate lung epithelial and endothelial permeability, facilitate endothelial repair and reduce inflammation. Another characteristic is that they can release extracellular vesicles (exosomes) which envelop cytokines and growth factors.
One approach that has been under study is the use of genetically modified MSC to improve some of their characteristics. One of the abilities of MSC is their ability to home to the site of damage so systemic delivery of MSC is the most commonly used. This means that the cells can travel to the area where there is inflammation.
Their low immunogenicity and preferential migration to the site of damage are two important factors that make the treatment with MSC very promising. There are some ongoing studies evaluating the properties and potential benefits of the use of MSC for ARDS because of the lack of current specific treatment for the condition. One example of a disease that can lead to ARDS is the SARS-Cov-2 infection which continues to be a major concern worldwide and for which there is no treatment, other than supportive measures.
Source: Han J, Liu Y, Liu H, Li Y. Genetically modified mesenchymal stem cell therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):386.
Source link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6915956/