Regenerative Medicine News and General Information
Exosomes and their Role in Skin Regeneration and Immunomodulatory Therapy
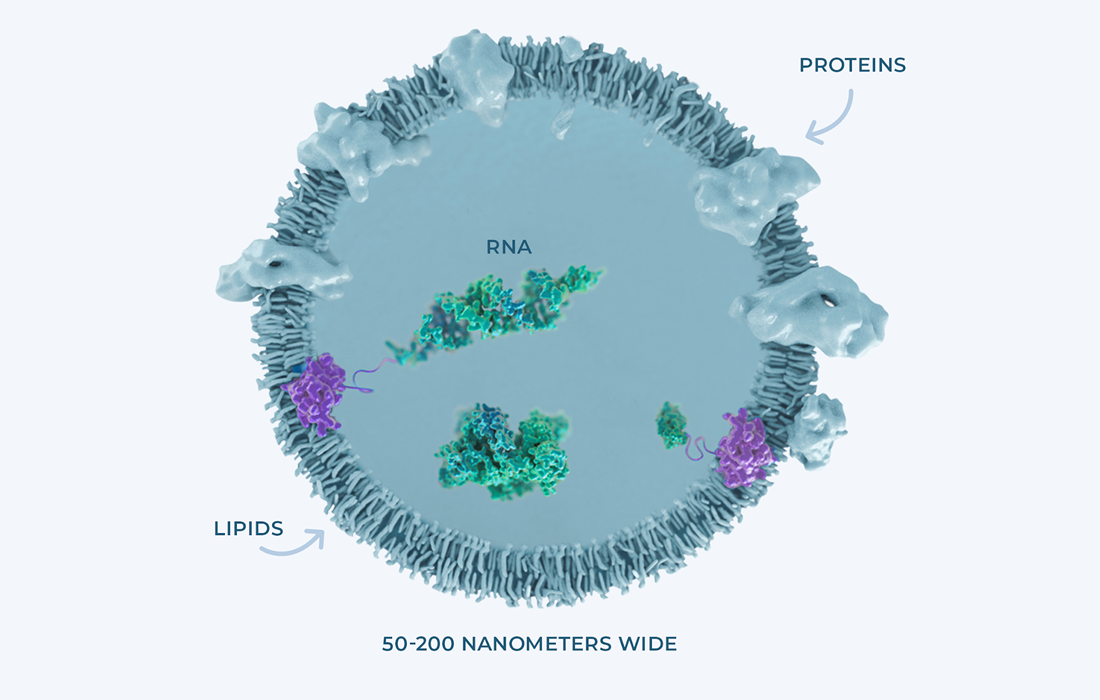
Exosomes are nano-sized vesicles that serve as mediators for cell to cell communication. They have unique nucleic acids, proteins and lipids that reflect their characteristics of producer cells. They can be used as cell-free therapeutics.
Mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes have gained great attention due to their immunomodulatory and regenerative functions. Many studies have shown anti-inflammatory, anti-aging and wound healing effects.
The extracellular vesicles or exosomes were discovered back in the 1940s and began to draw significant attention after the discovery of their role in cell to cell communications. Their mode of action for therapeutic effects of stem cells is mainly paracrine effects (a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells) by secreted factors from stem cells.
Mesenchymal stem cell-exosomes can be isolated from different tissues such as: bone marrow, umbilical/placental tissues, adipose tissue, embryonic stem cells and others.
Some examples of the different properties and clinical uses of exosomes are:
- Anti-Inflammation and immunomodulation: It has been demonstrated that MSCs have the property of intrinsic immunosuppressive capabilities to alleviate inflammation and immune responses. MSC-exosomes can be an excellent alternative to MSC cell therapy since MSC-exosomes possess similar biological functions, while they are more stable and have lower immunogenicity.
- T Cell Regulation: MSC-exosomes modulate functions or activities of T cells by suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β, and an increase of anti-inflammatory cytokines TGF-β.
- Inflammation in Skin: Human bone marrow MSC-exosomes reduce photoaging and inflammation in mice models which might be helpful to prevent and treat cutaneous aging. They were also reported to enhance angiogenesis (creation of new blood vessels).
MSC-exosomes orchestrate all phases of skin wound healing because of their ability to modulate inflammation, activate migration and proliferation of various cells.
- Anti-Aging Effects: One of the hallmarks of the aging process is the cellular senescence. It is a state of the cycle of every cell in which the cell is not able to grow and regenerate. The cell starts having a response known as senescence-associated secretory phenotype that contributes to the process of aging. Interventions that suppress this inflammatory response have a potential to alleviate chronic diseases.
Recently it was demonstrated that exosomes from young mice plasma extender the lifespan of old mice by delaying aging. More importantly, growing evidence suggests that cellular senescence can be alleviated or reversed by EVs or exosomes derived from stem cells.
Mesenchymal stem cell-exosomes are now widely accepted as next-generation cell-free therapeutics for intractable diseases. Continuous research it’s been conducted in order to determine the therapeutic effects and accurate quantity of exosomes needed for their appropriate use. They may provide a completely new therapeutic paradigm for human healthcare.
Source:
Ha DH, Kim HK, Lee J, et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes for Immunomodulatory Therapeutics and Skin Regeneration. Cells. 2020;9(5):1157. Published 2020 May 7.
Source link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7290908/
Images from: https://www.codiakbio.com/our-science/exosomes-explained