Platelet-Rich Plasma
Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder essentially triggered by the activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) which in turn triggers a series of inflammatory reactions leading to the disease process.
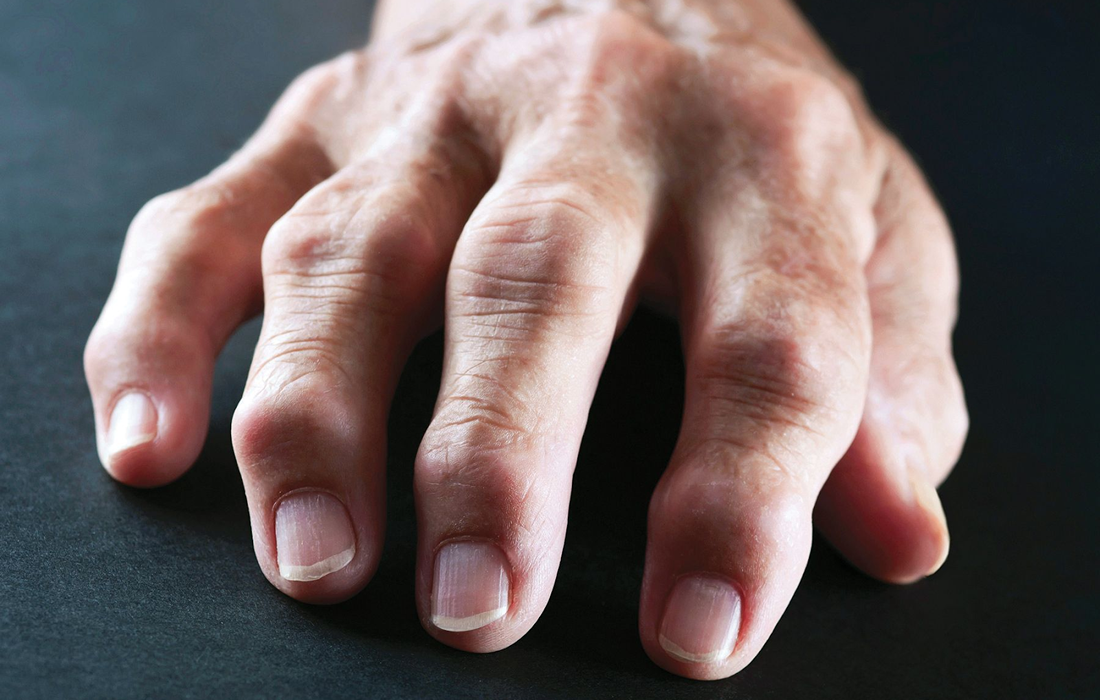
It is a chronic inflammatory disorder that can affect more than just the joints. In some people, the condition can damage a wide variety of body systems including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
Unlike the wear-and-tear damage of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of your joints, causing a painful swelling that can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity.
The inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis is what can damage other parts of the body as well. While new types of medications have improved treatment options dramatically, severe rheumatoid arthritis can still cause physical disabilities.
Current Treatment Options
The treatment of the disorder has been closely evolving with an understanding of its pathogenesis. Before the middle of the 1980s, the drugs used were non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and steroids. Then the main modality of treatment was through the disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Decoding the molecular basis of inflammation in RA opened new arenas in its management with the introduction of biologic DMARDs. These medications are rapidly acting but they can cause several side effects. Also, their cost limits their use as first-line medications. Some examples of these medications include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, and sulfasalazine.
Other commonly used medications are non-steroidal antiinflammatories (NSAIDs) for pain management and steroids, such as prednisone. Both of them can cause several side effects and do not change the course of the disease.
Use of Regenerative Medicine
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has been used and studied for many years in different medical specialties, including orthopedics, sports medicine, and dermatology.
PRP has shown in multiple studies that the factors that contain, released by platelets can stop inflammation, reverse the inflammatory changes and accelerate the natural healing process.
Platelets have immunomodulatory properties. In RA, their number and activation correlate with the disease activity. The proinflammatory products released in RA and the products of articular cartilage degradation lead to recruitment and dysregulated activation of platelets. There also exists crosstalk between the immune cells and platelets by which platelets modulate both innate and adaptive immunity.
Research Studies
Available animal studies on pigs, rats, and mice show encouraging molecular, histologic, and clinical results. There has been no evidence of exacerbation of inflammation in these studies.
The only study on the effects of PRP on RA in human subjects is a case series by Badsha et al in 2019. They administered the PRP to four RA patients in seven joints who had an inadequate response to intra-articular steroid injections. All the patients were on oral anti-rheumatoid drugs before and after the steroid and PRP injection. Three of the patients had immediate pain relief with improvement in synovial changes, while the third patient had only improvement in synovial changes, while VAS remained the same.
Preclinical studies have shown a decrease in the disease activity and with no major adverse reactions presented. Also, in vitro studies have shown suppression of inflammation. The available research is encouraging towards the use of PRP in RA, but larger trials are needed to understand the exact role of platelets in the disease pathogenesis and to standardize the treatment for RA. Nevertheless, results from animal studies hold promise for the treatment of this condition, for which current therapeutic options don’t work for many patients.
Sources:
Chellamuthu G, Muthu S, Khanna M, Khanna V. “Platelet-rich plasma holds promise in management of rheumatoid arthritis”-systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2021 Nov;41(11):1895-1903. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04849-9. Epub 2021 Apr 8. PMID: 33834280.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353648
Image from:
https://www.webmd.com/rheumatoid-arthritis/features/ra-diagnosis-doctor-perspective