Regenerative Medicine News and General Information
Why is Oral Health important even for systemic diseases?
The oral cavity is colonized by billions of bacteria, fungi, and even viruses, now known as oral microbiomes. It is well known that the oral microbial community includes pathogenic bacteria and probiotics, and that the homeostasis of oral microbiomes plays a crucial role in maintaining the well being and healthy status of a human.
There is strong evidence that once the balance of the oral microbiota is broken, predominant pathogens can lead to oral diseases like periodontitis, caries and infections. Furthermore, several studies suggest that Porphyromonas gingivalis may be a driving factor in the development of digestive tract cancer.
Probiotics are a type of microorganisms that are beneficial to our health and that can produce health care effects at a proper dose. Some examples are: Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterias, Escherichia coli. They maintain the balance of host bacteria by secreting antimicrobial substances and modulating our immune response. The balance between pathogenic bacteria and probiotics is very indispensable to maintain oral health.
It has been reported that the wound healing process is delayed as a result of disturbances of the oral microbiota. Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) are considered as a promising method with the potential to promote tissue regeneration and wound healing. Studies have shown that the balance of oral microbiota can activate functions of MSC and that one of them is the promotion of wound healing.
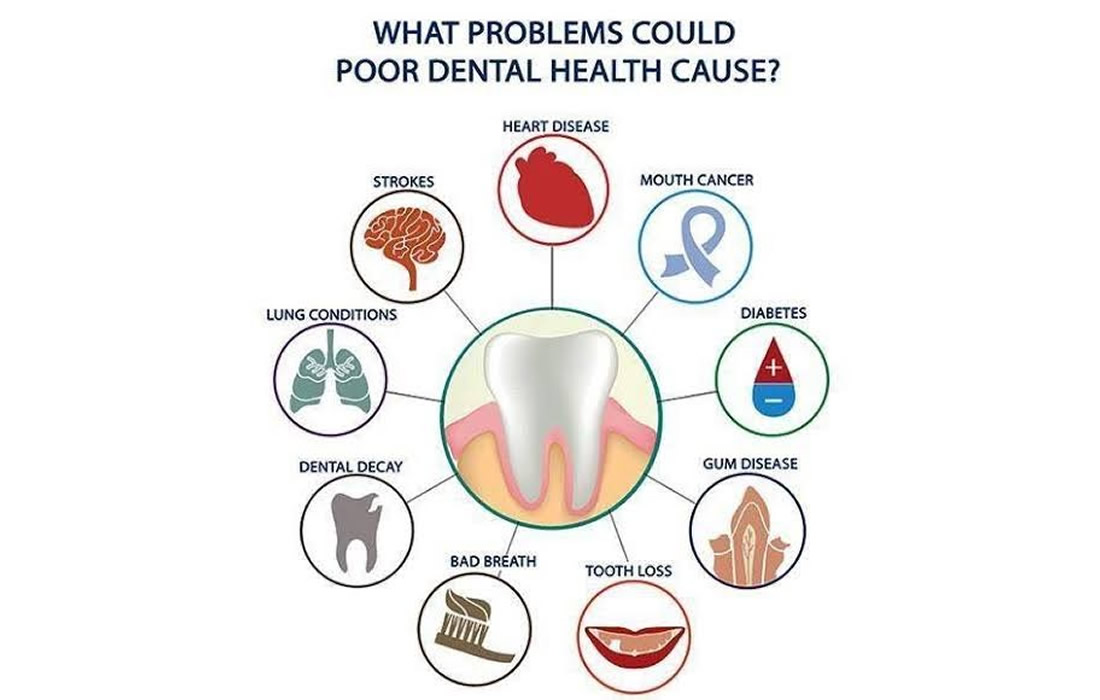
Studies have shown that periodontal disease may be linked to cardiovascular disease, stroke, bacterial pneumonias, and other conditions. Research suggests that people with periodontal disease are nearly three times as likely to suffer from a heart disease. Theres also evidence that moderate to severe periodontitis tends to increase the level of systemic inflammation which could potentially lead to systemic conditions. This is why it is so important to maintain proper Oral health.
Source: Han N, Jia L, Guo L, Su Y, Luo Z, Du J, Mei S, Liu Y. Balanced oral pathogenic bacteria and probiotics promoted wound healing via maintaining mesenchymal stem cell homeostasis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Feb 14;11(1):61.
Source link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7023757/