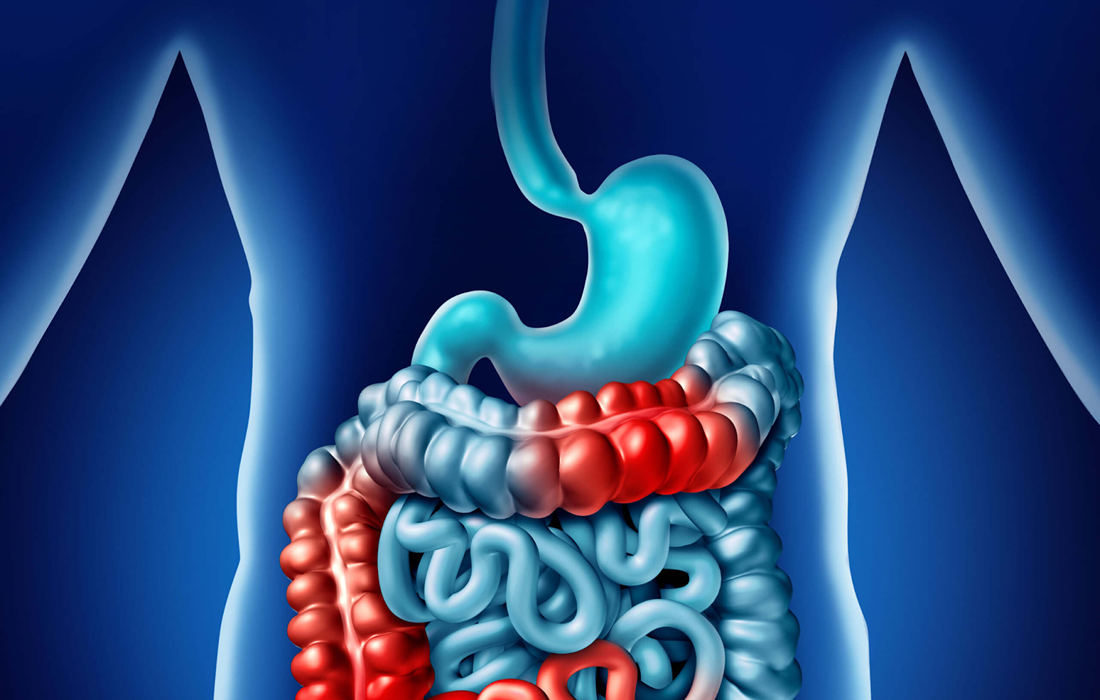
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) and is a complex, multifactorial, immune-mediated illness . There are approximately 6.9 million IBD cases globally, and this number is rising. Currently, it is estimated that 780,000 patients in the United States suffer from CD, and 33,000 new cases are diagnosed each year […]
Author Archives: Gabriel Piña, MD
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient involved in many biological processes, most notably helping our body absorb minerals, such as calcium and magnesium. While some of the vitamin D we need is made in the body from sunlight, vitamin D deficiencies are often treated with supplementation. Evidence from laboratory studies, epidemiologic research and clinical research […]
A team of researchers, affiliated with UNIST has recently unveiled a hemolysis-free and highly efficient blood plasma separation platform. Published in the May 2021 issue of Small, this breakthrough has been led by Professor Joo H. Kang and his research team in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at UNIST. The research team expects that the […]
Over the last few decades, the prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults has increased worldwide. Over 2 billion adults are overweight, while over 650 million are obese. Metabolic syndrome is characterized by visceral obesity, hypertension, atherogenic dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and glucose intolerance, raising the risk of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Convincing data suggest […]
Published in Aging Cell, the findings show that animals treated with rilmenidine, currently used to treat hypertension, at young and older ages increases lifespan and improves health markers, mimicking the effects of caloric restriction. They also demonstrate that the healthspan and lifespan benefits of rilmenidine treatment in the roundworm C. elegans are mediated by the […]
Traumatic injury to the brain, spinal cord and optic nerve in the central nervous system (CNS) are the leading cause of disability and the second leading cause of death worldwide. CNS injuries often result in a catastrophic loss of sensory, motor and visual functions, which is the most challenging problem faced by clinicians and research […]
As the population continues to age, a pandemic of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is emerging, with conservative estimates of over 14 million victims globally by 2040. While PD patients display a wide range of non-motor features, the defining symptoms are progressive motor deficits due to striatal dopaminergic insufficiency secondary to loss of dopaminergic nigral neurons. Current […]
Nitrites and nitrates occur naturally in water and soil and are commonly ingested from drinking water and dietary sources. They are also used as food additives to increase shelf life. A study publishing January 17 in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Bernard Srour of the Nutritional Epidemiology Research Team (EREN-CRESS) of Inserm, INRAE, […]
Pulmonary fibrosis is a fatal disease that thickens and scars healthy lung tissue, creating inflammation and replacing the lining of the lung cells with fibrotic tissue. In the last five years, Ke Cheng and his lab developed spheroid-produced lung stem cells (LSCs) as a potential therapeutic for pulmonary fibrosis. Cheng is Randall B. Terry Jr. […]
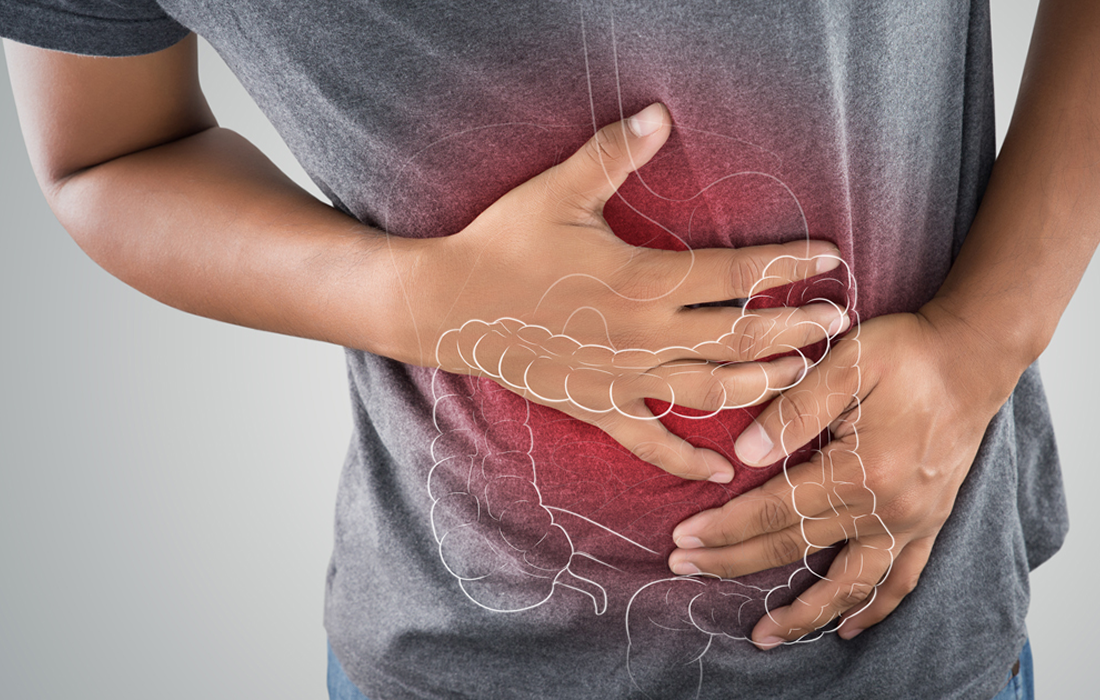
People with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) have lower bacterial diversity in the intestine than do healthy people, according to a team of Korean investigators. The investigators believe that theirs is the first analysis to find a clear association between IBS and reduced diversity in the microbiota of the gut. The research appears in Microbiology Spectrum, […]