Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia that affects more than 6.5 million Americans, according to the Alzheimer’s Association. To find effective treatments and slow the progression of this debilitating disease, researchers have made much progress in developing new drugs that target beta-amyloid plaques, one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Beta-amyloid plaques […]
Monthly Archives: September 2023
While aripiprazole has long been a standard treatment for psychiatric disorders, recent studies indicate that it is effective in treating circadian rhythm sleep disorders, including delayed sleep-phase syndrome. This condition causes patients to sleep and wake extremely late at times. Researchers from the University of Tsukuba have discovered that aripiprazole can directly affect the mammalian […]
Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health researchers have successfully created chimeric embryos containing a combination of human and pig cells. When transferred into surrogate pig mothers, the developing humanized kidneys had normal structure and tubule formation after 28 days. The work appears in the journal Cell Stem Cell. The researchers focused on kidneys because they […]
A healthy lifestyle that involves moderate alcohol consumption, a healthy diet, regular physical activity, healthy sleep and frequent social connection, while avoiding smoking and too much sedentary behaviour, reduces the risk of depression, new research has found. In research published today in Nature Mental Health, an international team of researchers, including from the University of […]
In a new study researchers used data from a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of RA susceptibility to construct a polygenic risk score (PRS). They evaluated the PRS’s ability to predict radiographic progression — progressive anatomical damage assessed by radiographic imaging — in individuals with RA. In a GWAS, genomic analysis of a group of individuals […]
106 adults with T2D were randomly assigned to either the high-protein or normal-protein diet for 52 weeks. Both diets were energy-restricted. The high-protein diet included recommendations to include lean beef in the diet, while the normal-protein diet instructed participants to refrain from eating any red meats. The team of researchers found that both a high-protein […]
Researchers from the University of Arizona Cancer Center have identified a new method of activating specific molecules to target cancer cells while leaving healthy cells unharmed. In their recent study, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, Wei Wang, PhD, and his team developed a new strategy called click-release proteolysis targeting chimeras, or […]
A world-first discovery has revealed special immune cells called ‘killer T cells’ in older adults, directed against influenza viruses, closely resemble those found in newborns and children, but struggle to recognise infected cells — a finding that unlocks the potential for the development of better vaccines and therapies tailored to different age groups. Killer T […]
Millions of Americans have inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which occurs in one of two forms: Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. Though the two have similar symptoms, they require different treatment strategies, and tests to distinguish between them are invasive. Though Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis have similar symptoms and unknown causes, they affect disparate parts […]
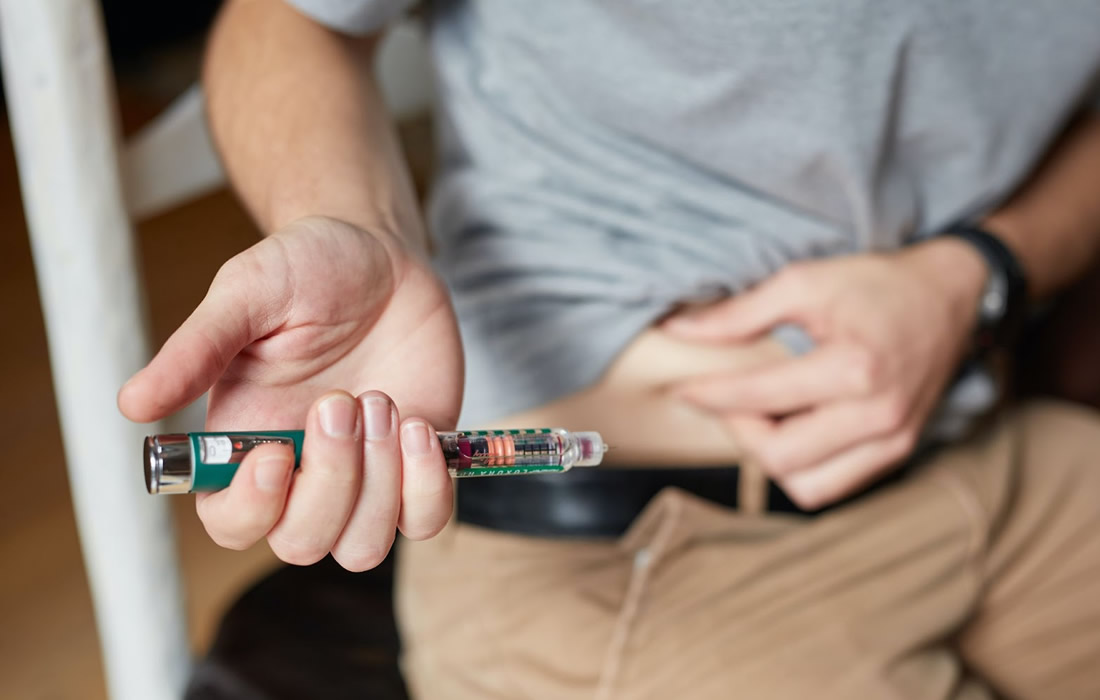
Treating newly diagnosed Type 1 diabetes patients with semaglutide may drastically reduce or even eliminate their need for injected insulin. A total of 10 patients at UB’s Clinical Research Center in the Division of Endocrinology were studied from 2020 to 2022, all of whom had been diagnosed in the past three to six months with […]