The path a cell takes from healthy to metastatic cancer is mostly driven by epigenetic changes, according to a new computational study. Dr. Eduard Porta, group leader of the Cancer Immunogenomics group at the Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute, participated in the new analysis that has been recently published in the journal Nature. Every cell […]
Author Archives: Karely Vega, MD
LMU researchers have identified a signaling pathway by which aspirin can inhibit colorectal cancer. Colorectal cancer (bowel cancer) is the third most common form of cancer worldwide, with around 1.9 million newly diagnosed cases and 900,000 deaths every year. Therefore, preventive substances represent an urgent clinical need. Aspirin/acetylsalicylic acid has proven to be one of […]
Imagine a skin cream that heals damage occurring throughout the day when your skin is exposed to sunlight or environmental toxins. That’s the potential of a synthetic, biomimetic melanin developed by scientists at Northwestern University. In a new study, the scientists show that their synthetic melanin, mimicking the natural melanin in human skin, can be […]
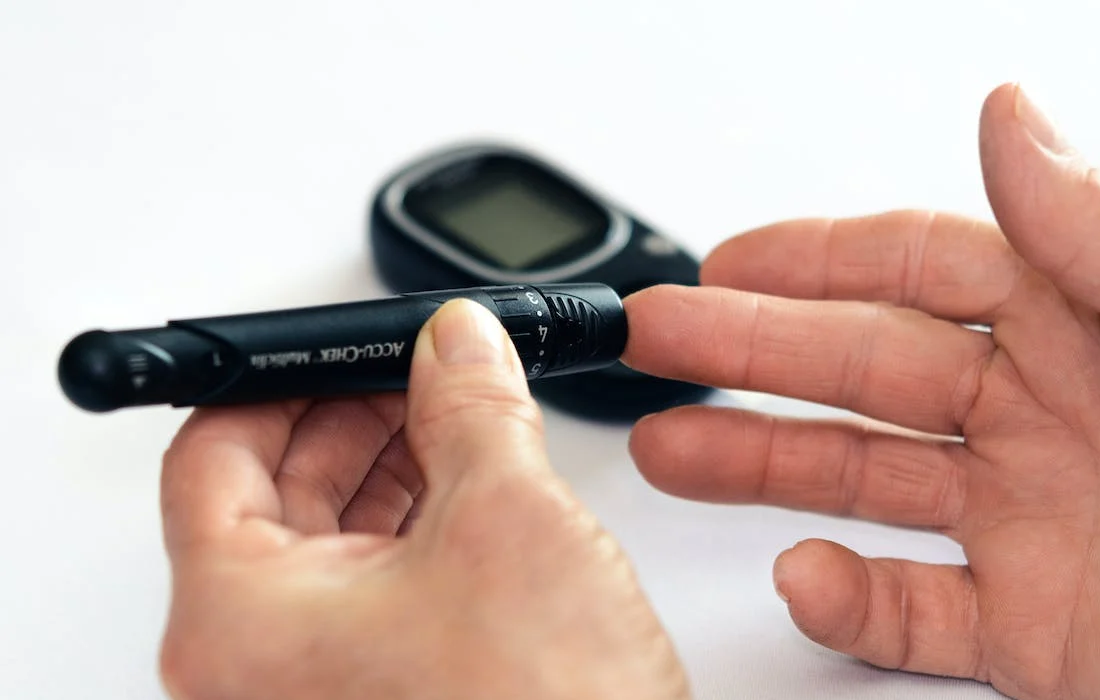
A University of Alberta team has developed a new step to improve the process for creating insulin-producing pancreatic cells from a patient’s own stem cells, bringing the prospect of injection-free treatment closer for people with diabetes. The researchers take stem cells from a single patient’s blood and chemically wind them back in time, then forward […]
A new study from researchers at the University of British Columbia’s Faculty of Medicine reveals a direct link between high insulin levels, common among patients with obesity and Type 2 diabetes, and pancreatic cancer. The study, published in Cell Metabolism, provides the first detailed explanation of why people with obesity and Type 2 diabetes are […]
Those at risk for Type 2 diabetes may already know to avoid sugar, but new research suggests they may want to skip the salt as well. A new study from Tulane University published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings found that frequently adding salt to foods was associated with an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. […]
Lack of sleep is a global problem. Researchers estimate two-thirds of all adults occasionally experience insomnia symptoms, and between 50 to 70 million Americans have a recurring sleep disorder, such as sleep apnea or insomnia. Insufficient sleep has been linked to seven of the 15 leading causes of death in the U.S., such as cardiovascular […]
Multiple studies attest that consuming plant foods may reduce chronic illnesses such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers. Researchers at the University of Minnesota in St. Paul, MN, have now uncovered additional benefits of insoluble fiber beyond improving stools and laxation. In their recent review study, the experts found that bioactives in […]
An international study led by the University of Granada has identified for the first time the optimal number of steps at which most people obtain the greatest benefits, and also shows that the pace at which you walk provides additional benefits. The idea that you should take 10,000 steps a day originated in Japan in […]
Current osteoarthritis treatment manages symptoms rather than addressing the underlying disease, but a new University of Adelaide study has shown the condition may be treatable and reversible. Osteoarthritis is a long-term and progressive condition which affects people’s mobility and has historically had no cure. Often described as a ‘wear and tear’ condition, factors such as […]