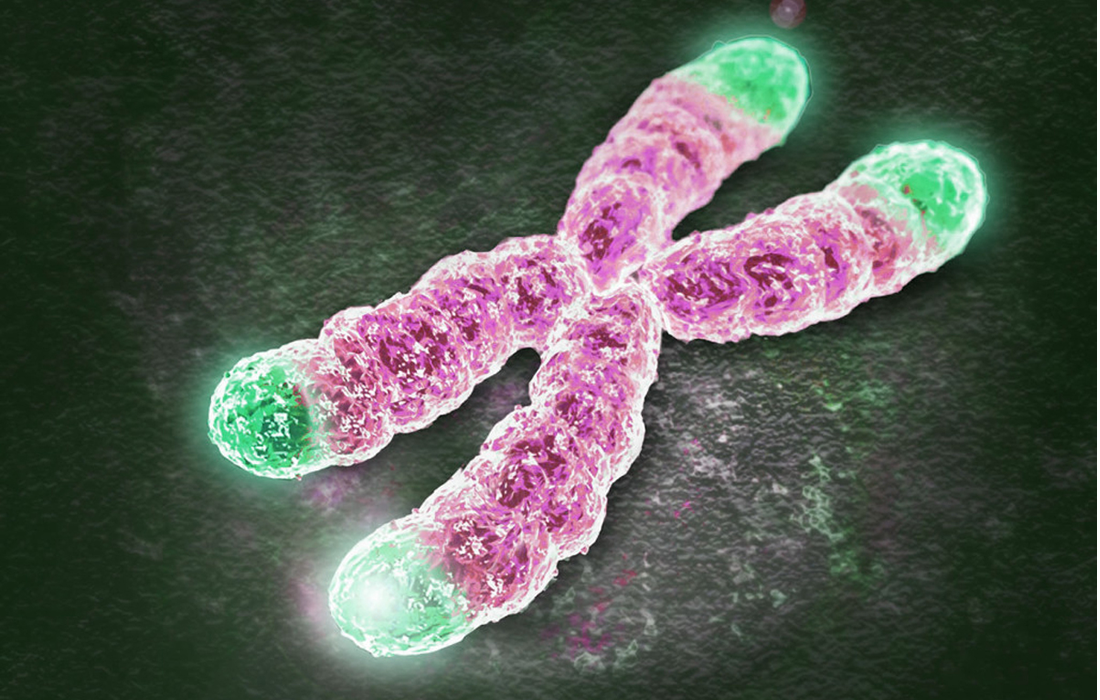
What are Telomeres? Telomeres are non-coding repetitive DNA sequences at the ends of chromosomes that protect DNA ends from degradation by exonucleases or end-to-end fusions. When a cell divides, its chromosomes, the bundles of DNA that encode genes, get a little shorter. This is because the cellular machinery for duplicating DNA cannot copy the molecule […]
Category Archives: Anti-Aging
Reduced caloric intake without malnutrition is the oldest known life span–extending intervention. Laboratory studies throughout the 20th century established and confirmed the benefits of caloric restriction (CR) in multiple model systems. CR not only increased life span across evolutionarily distant organisms but also reduced age-associated disease burden and functional decline in these studies. Epidemiological data […]
The survival and reproductive success of all organisms depend upon their ability to obtain food. Accordingly, animals have evolved behavioral and physiological adaptations that enable them to survive periods of food scarcity or absence. When food is not available for extended periods some organisms become dormant; for example, yeast enters a stationary phase, nematodes enter […]
Cumulative stress can have different psychiatric and physical effects, increasing the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, mood disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder and addiction. Stress may reduce psychological resilience measures such as emotion regulation and self control that are known to protect against psychiatric and physical health outcomes. Notably, emotional stress exposure decreases cognitive and emotion regulation […]
Dyslipidemias are a major risk factor for the development of cardiovascular (CV) atherosclerotic diseases. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) is considered the major causative lipid fraction, and lowering it reduces the risk of CV events. LDL is therefore the preferred risk marker in the international guidelines. But with the newly updated guidelines, attention is also recommended […]
Aging is one of the biggest risk factors for chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative pathologies and diverse types of cancers. In recent years, big progress has been made to develop agents to treat individual age-related conditions, such as diabetes, osteoporosis, skeletal fragility and vascular dysfunction. However, the effect has been modest. Several […]
Reduced caloric intake without malnutrition is the oldest known life span–extending intervention. Laboratory studies throughout the 20th century established and confirmed the benefits of caloric restriction (CR) in multiple model systems. CR not only increased life span across evolutionarily distant organisms but also reduced age-associated disease burden and functional decline in these studies. Epidemiological data […]
What is Senescence? Senescence is an irreversible proliferation arrest and a key restriction mechanism to prevent the propagation of damaged cells. However, the progressive accumulation of senescent cells with time has been associated with loss of tissue homeostasis, and is known to contribute to the functional impairment of different organs typically seen in ageing. Research […]
In aging, B- cell regeneration is regulated by communication between peripheral B cells and progenitors in the bone marrow. Loss of B lymphocyte regeneration in the bone marrow (BM) is an immunological hallmark of advanced age, which impairs the replenishment of peripheral B-cell subsets and results in impaired humoral responses, contributing to immune system dysfunction […]
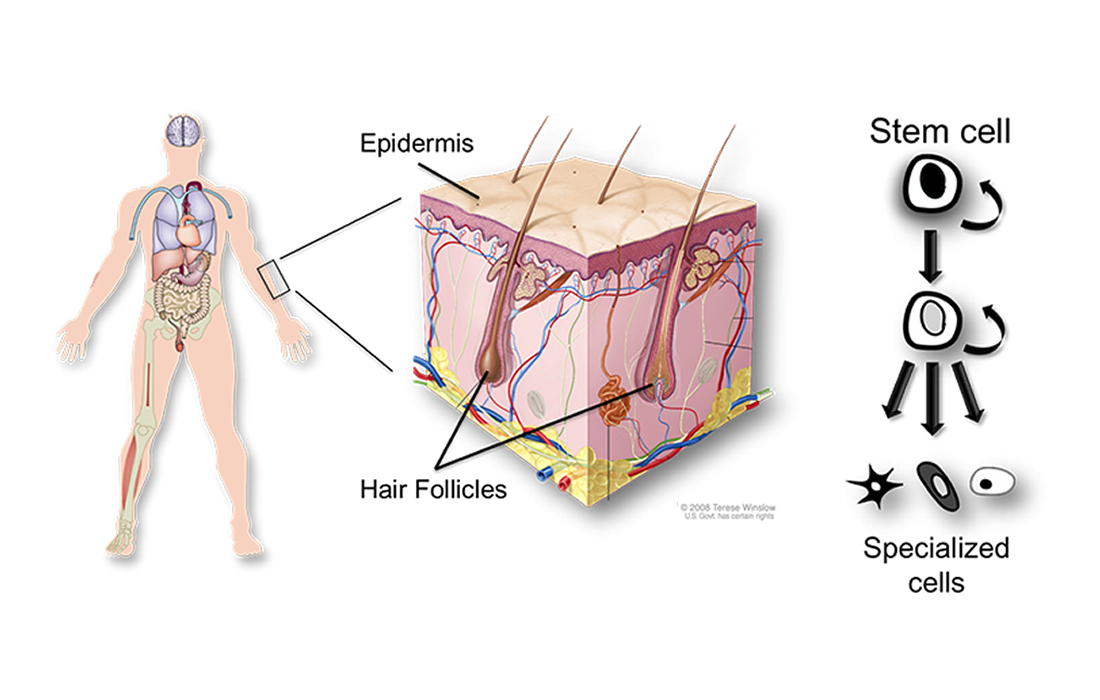
The skin is a complicated organ composed of various kinds of cells and has three layers, the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous adipose tissue. The skin covers the whole body as a barrier and plays important roles in protection from environmental factors including physical and chemical stimuli as well as ultraviolet rays. Recent studies have revealed […]