An international study, published in the journal of Science, has found that, after accounting for body size, energy expenditure peaks in infancy and then steadily declines until the age of about 20 years. Contrary to the popular belief that metabolism slows in middle age, the research suggests that energy expenditure does not change until close […]
Author Archives: Francisco Fernandez, MD
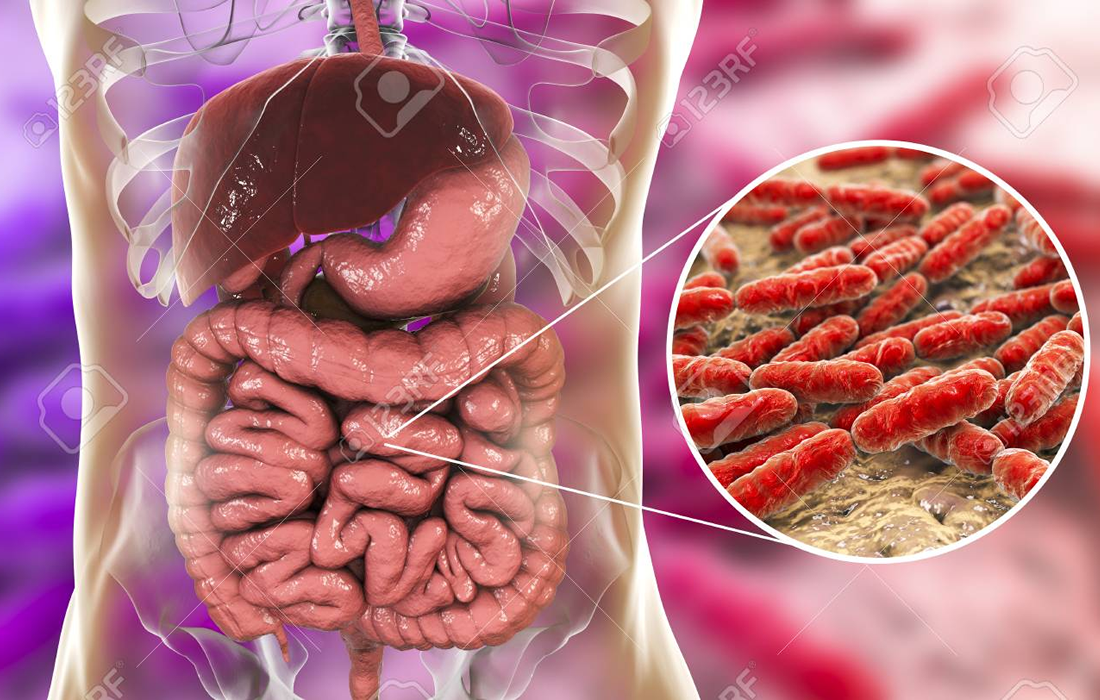
Understanding how diet affects gut microbes and thereby influences human health might lead to targeted dietary strategies. A clinical trial now provides some steps on the path towards this goal. Dietary fibre is the indigestible part of plant foods. Is mostly in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes. There are two types of fibre, soluble […]
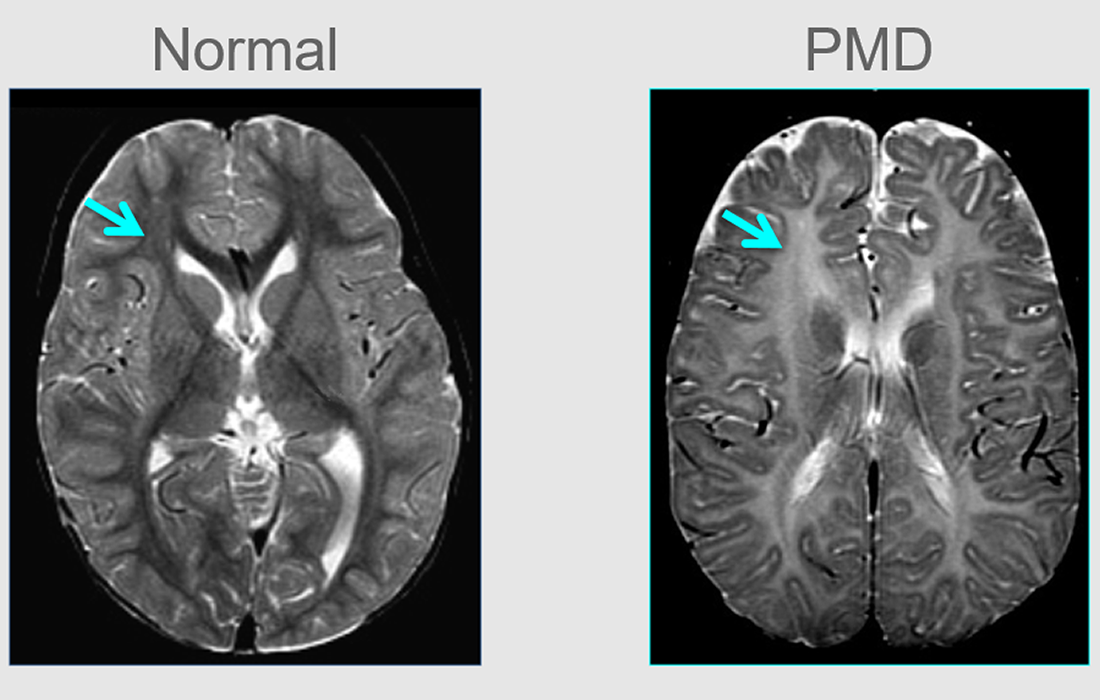
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD) is a rare, congenital X-linked recessive leukodystrophy caused by a mutation of the proteolipid protein 1 (PLP1) gene (Gencic et al., 1989), resulting in reduced levels of myelination without an inflammatory component or substantial volume loss of brain tissue. PMD is one of a group of hypomyelinating disorders (Helman et al., 2015), […]
Regenerative medicine has yet to designate biomarkers that can identify patients likely to respond to a stem cell therapy based on their expression of a clinical or molecular profile congruent with the therapeutic mechanism-of-action (MOA) of the stem cell for that condition, while withholding treatment from likely non-responders. Ultimately, such patient stratification will be required […]
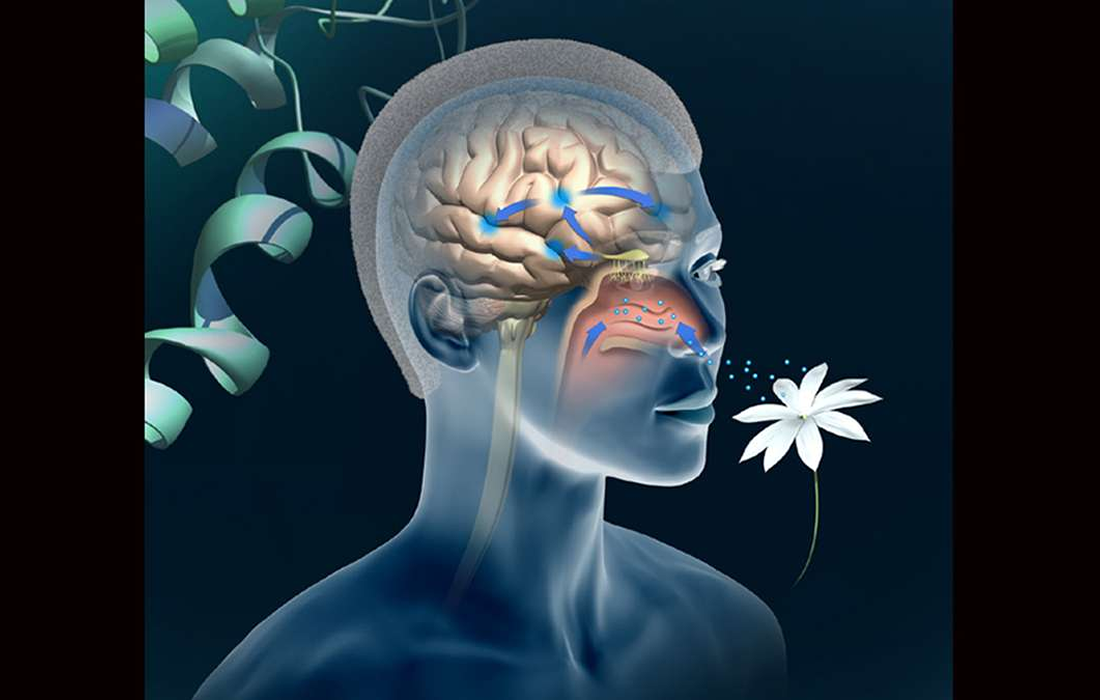
A stem cell therapy delivered into the nose can restore the sense of smell in a mouse model of olfactory loss. The findings were published in May 30 in the journal Stem Cells Reports and provide proof of principle for an approach that has the potential to be of broad utility for a range of […]
Feeding mice high-fructose corn syrup, a widely used sweetener in human diets, has been found to drive an increase in the surface area of the gut that is associated with enhanced absorption of dietary nutrients and weight gain. The incidence of obesity has been steadily increasing, tripling globally between 1975 and 2016, at a high […]
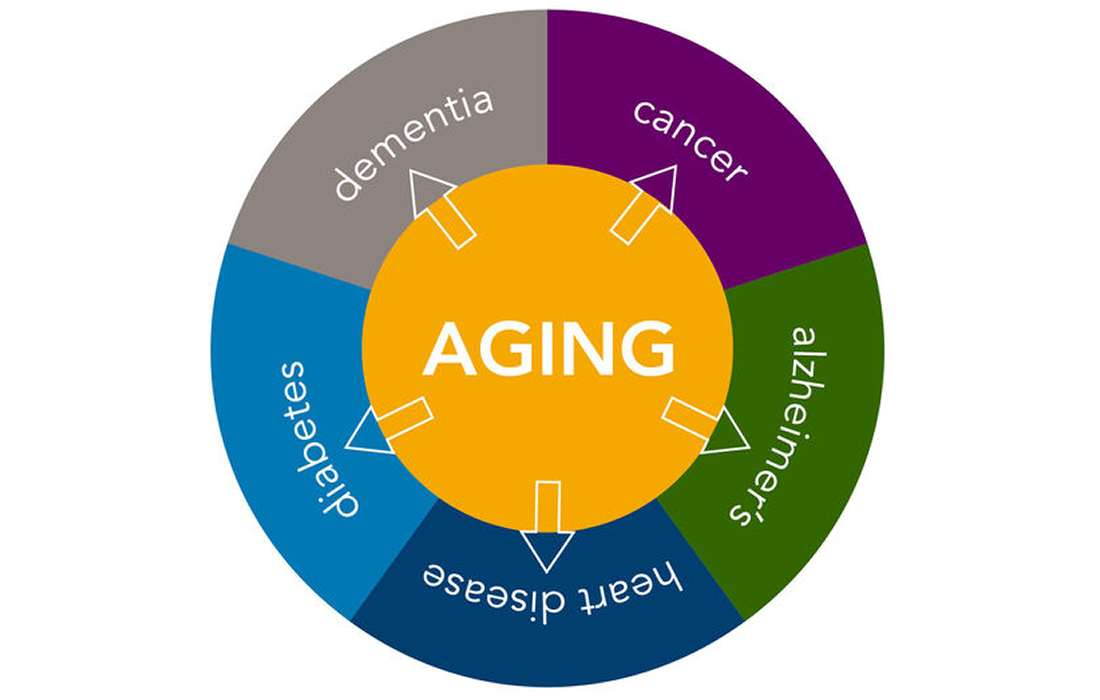
Parkinson’s disease (PD) stands in second place after Alzheimer’s disease among common neurodegenerative disorders. An overall incidence rate of 17 per 100,000 persons per year has been reported. The onset of PD is usually at 65 years or older, and it appears slightly more frequently in men than in women. The aging of society around […]
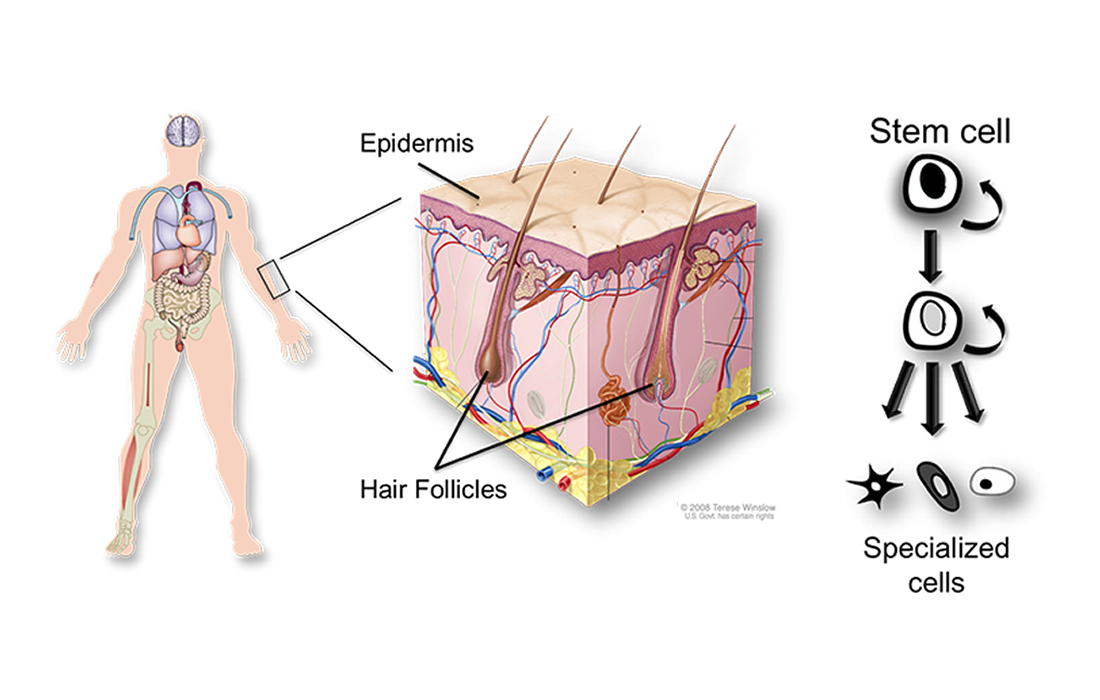
The skin is a complicated organ composed of various kinds of cells and has three layers, the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous adipose tissue. The skin covers the whole body as a barrier and plays important roles in protection from environmental factors including physical and chemical stimuli as well as ultraviolet rays. Recent studies have revealed […]
Redox and metabolic mechanisms lie at the heart of stem cell survival and regenerative activity. NRF2 is a major transcriptional controller of cellular redox and metabolic homeostasis, which has also been implicated in ageing and lifespan regulation. However, NRF2’s role in stem cells and their functioning with age is only just emerging. The importance of […]
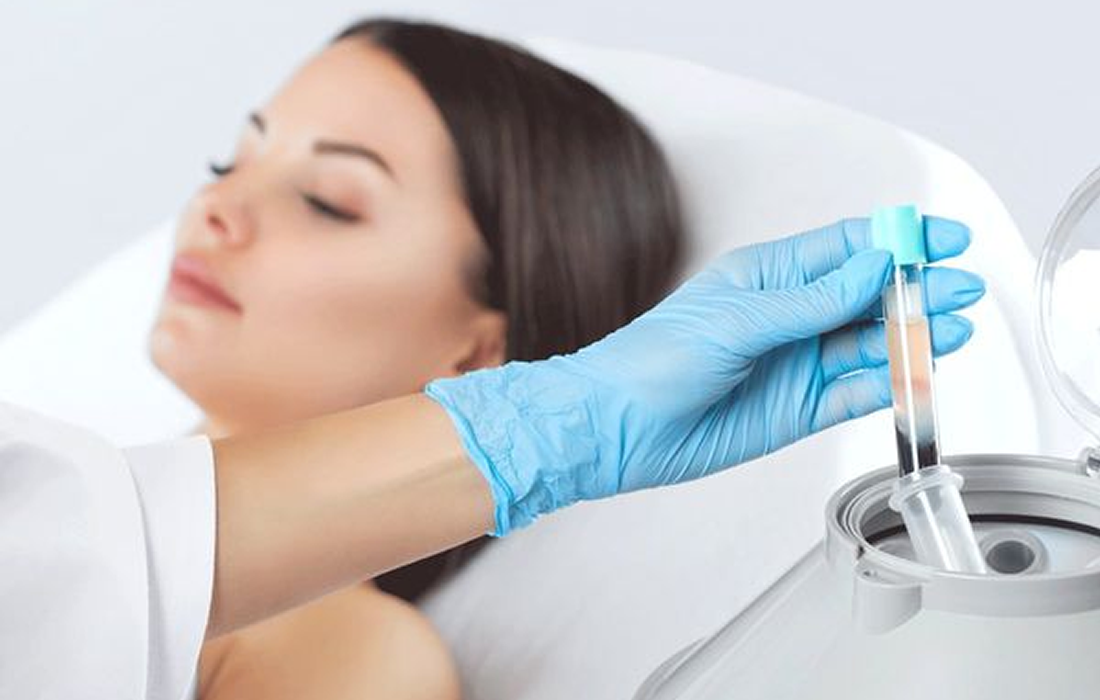
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is autologous blood plasma with a concentration of platelets well above baseline. The usual concentration of platelets in the blood is approximately 150,000 to 400,000 platelets per cubic microliter. PRP contains 4-7 times the physiologic concentration of platelets. PRP is prepared by centrifugation of blood drawn from the patient before any procedure […]