Hair loss (Alopecia ) occurs in more than 60% of men and in approximately 10% of women. Although a lack of scalp hair can potentially increase the risk of actinic damage and skin cancer, male and female pattern baldness are conditions that are, with few exceptions, treated electively. For millions of individuals, hair loss is […]
Author Archives: Gabriel Piña, MD
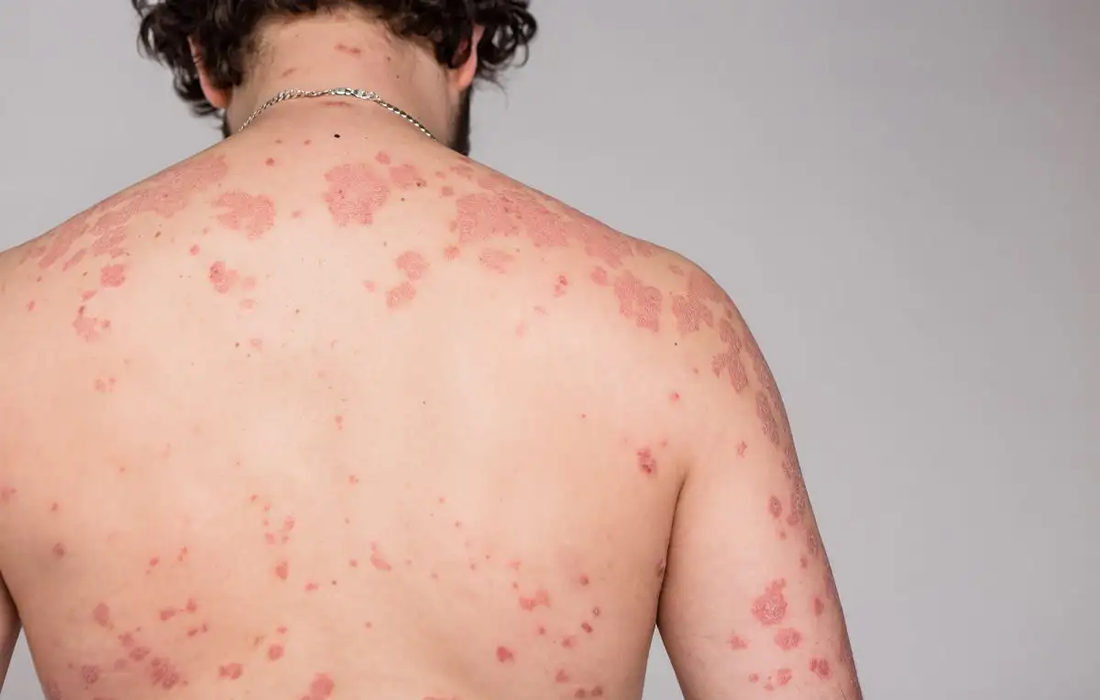
Psoriasis is a complex, chronic, multifactorial, inflammatory disease that involves hyperproliferation of the keratinocytes in the epidermis, with an increase in the epidermal cell turnover rate, and infiltrating immune cells that leads to secretion of various cytokines and chemokines including IL-17, IL-21, IL-22, IL-6, IL-1β, TNFα and CXCL1/3/5, which initiate a pro-inflammatory systemic response. Environmental, […]
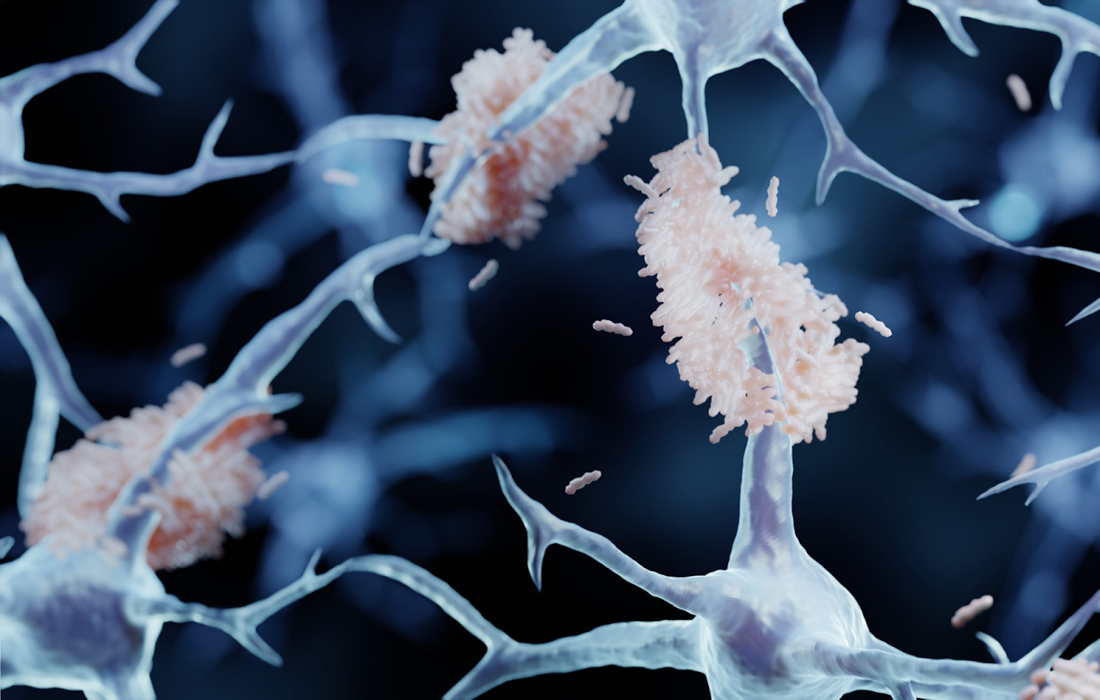
Dementia is considered a major neurocognitive disorder, in which a deficit in cognitive functioning is acquired rather than developmental. Dementia is most common in elderly individuals, with advancing age being the strongest risk factor. There are many types of this condition such as Alzheimer Dementia (AD) and Vascular Dementia (VD) , among others of all-cause […]
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of joint disease, affecting more than 30 million individuals in the United States alone. It can be thought of as primarily a degenerative disorder with inflammatory components arising from the biochemical breakdown of articular (hyaline) cartilage in the synovial joints. Osteoarthritis predominantly involves the weight-bearing joints, including the knees, […]
A recently published WHO report revealed that noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), such as cardio- and cerebral diseases, cancers, endocrine/metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes and obesity, account for 38 million deaths worldwide. Moreover the WHO predicts an increase in mortality caused by NCDs to 52 million in 2030. Fast progress of those impairments is mostly associated […]
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) describe carbohydrates as a major source of energy provided in the human diet, accounting for between 40 and 80% of the total energy requirements. On the other hand, there is a growing concern about the global rise in diet-related […]
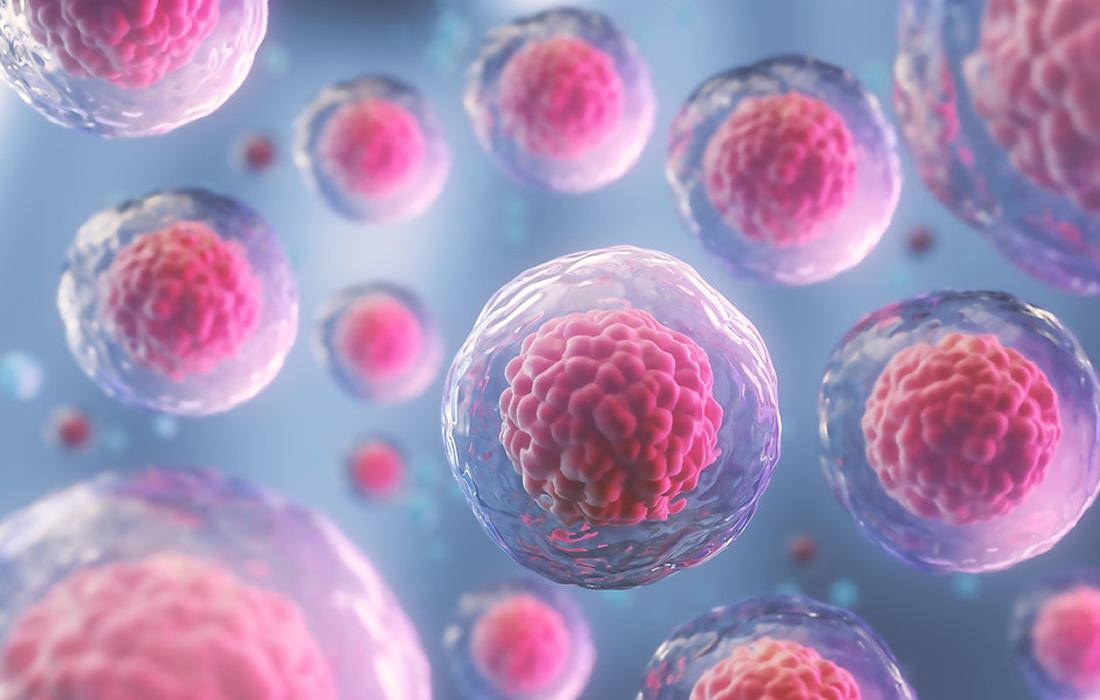
Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) possess the ability for unlimited self-renewal and differentiation to yield cells derived from the three germ layers . Upon adding specific growth factors, hESCs/iPSCs initiate differentiation and are converted into specific lineages. Recent progress in this field has successfully generated many functionally differentiated […]
Amyloid fibrils are protein polymers comprising identical monomer units (homopolymers). Functional amyloids play a beneficial role in a variety of physiologic processes (eg, long-term memory formation, gradual release of stored peptide hormones). Amyloidosis results from the accumulation of pathogenic amyloids. Amyloidosis is a clinical disorder caused by extracellular and/or intracellular deposition of insoluble abnormal amyloid […]
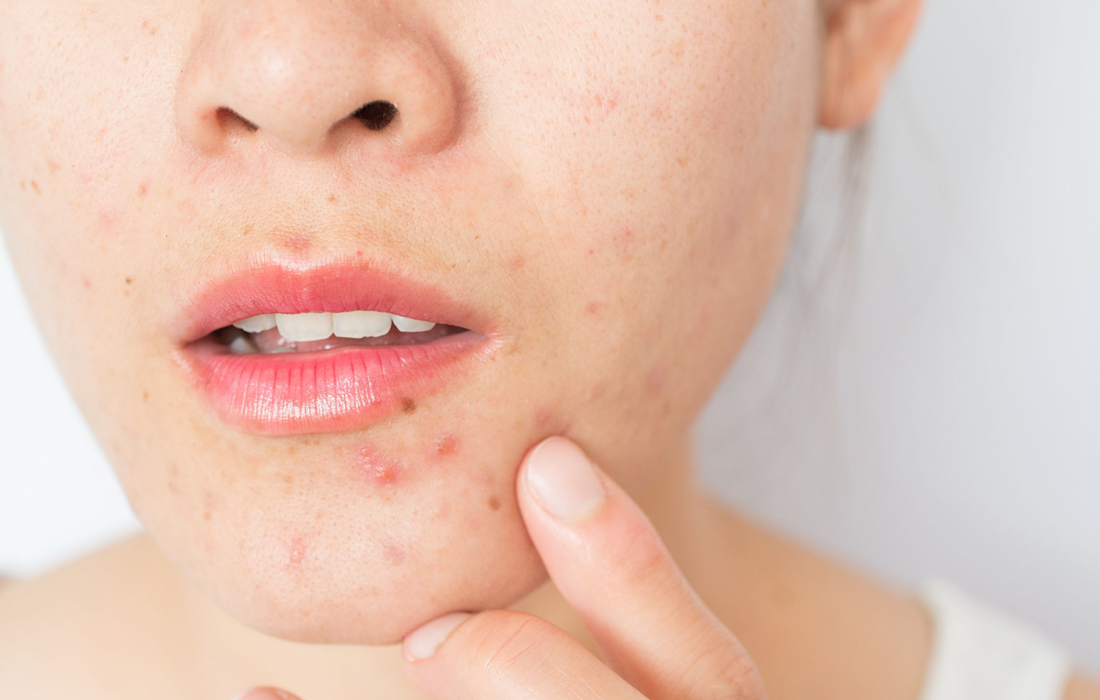
Acne vulgaris is characterized by noninflammatory, open or closed comedones and by inflammatory papules, pustules, and nodules. Acne vulgaris typically affects the areas of skin with the densest population of sebaceous follicles; these areas include the face, the upper part of the chest, and the back. It is the most common skin disease in the […]
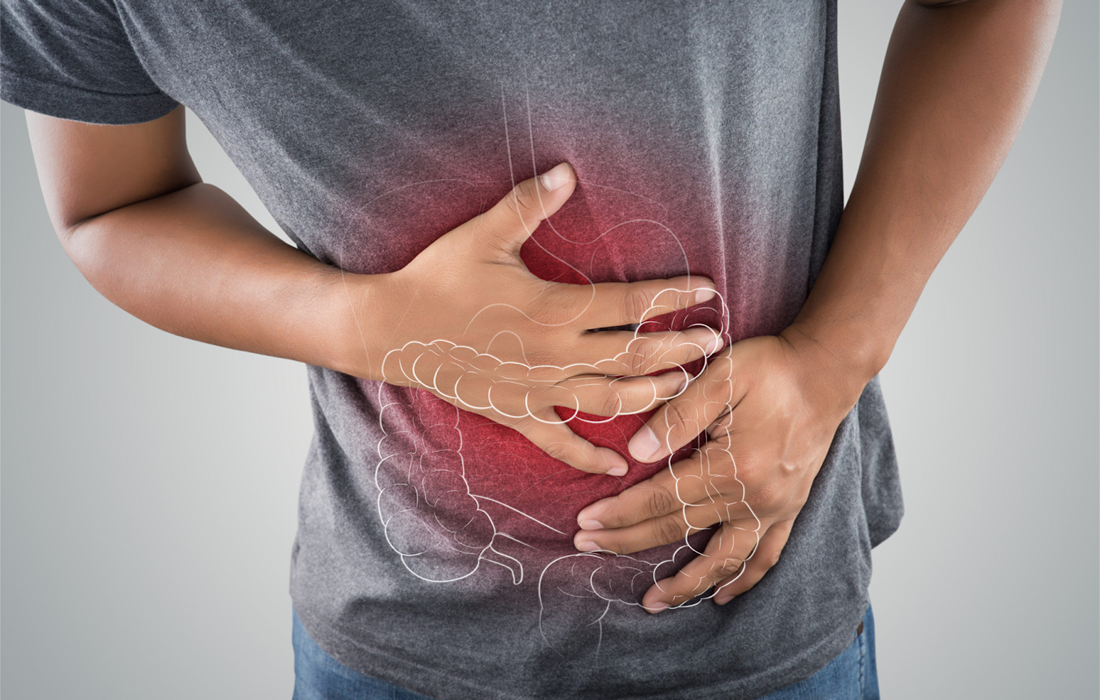
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a form of chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects more than 5 million patients worldwide. Studies have indicated that UC development is a long-term process that includes various unclear etiologies. Current therapies for ulcerative colitis (UC) fail to achieve satisfactory disease control. Selective inhibition of Janus kinase (JAK) type 1 […]