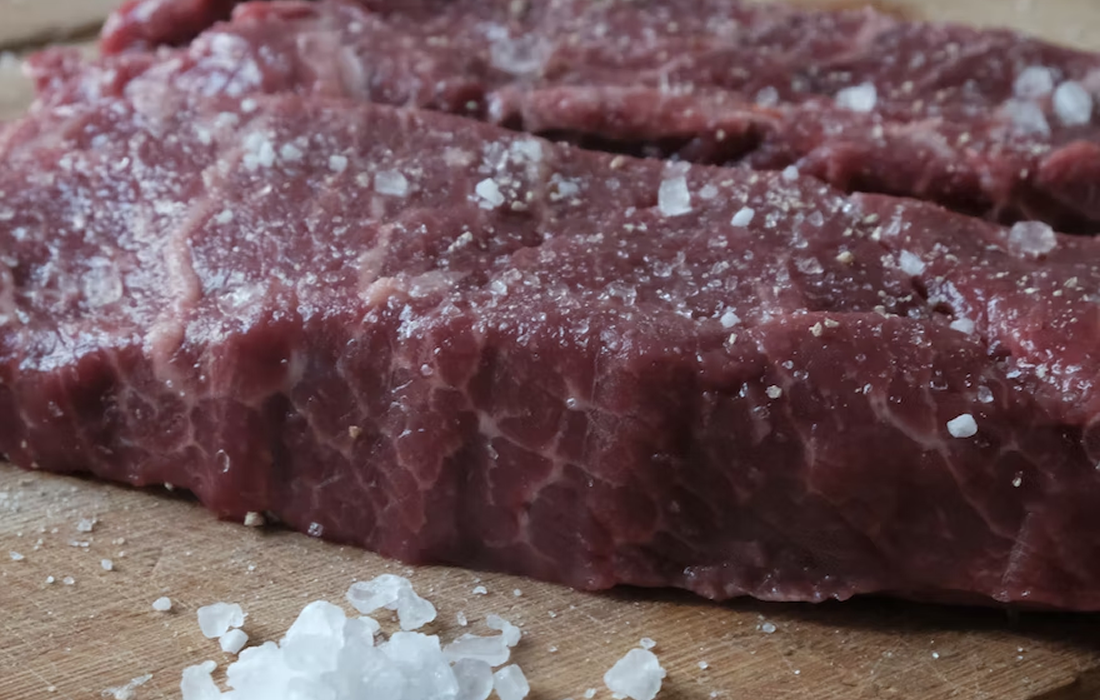
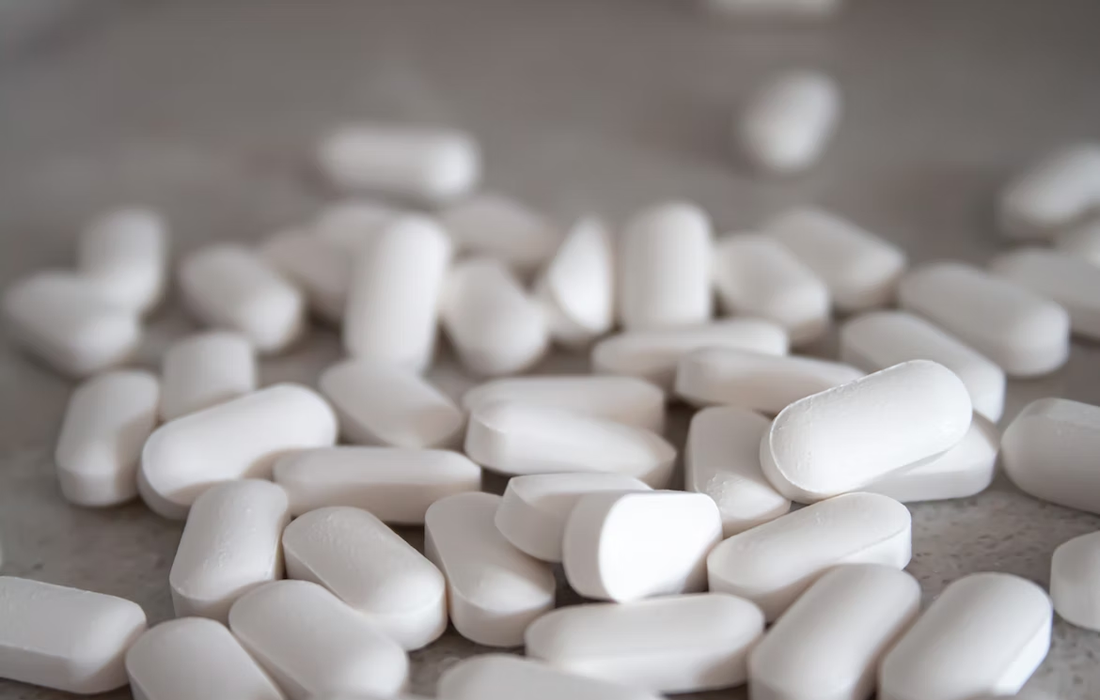
According to current WHO guidelines, adults should consume less than 2,000 mg of sodium per day (i.e. about 5 grams of traditional table salt), and at least 3,510 mg of potassium per day.Dietary salt substitutes not only lower blood pressure but also have a clear impact on hard clinical endpoints, lowering the risk of myocardial […]
Author Archives: Gabriel Piña, MD
Colorectal cancers remain the third most common cancer and third most common cause of cancer-related mortality in US men and women.In addition, rates of colon cancer in younger persons have been increasing. The incidence and mortality from colon cancer have been on a slow decline over the past several decades in the United States, with […]
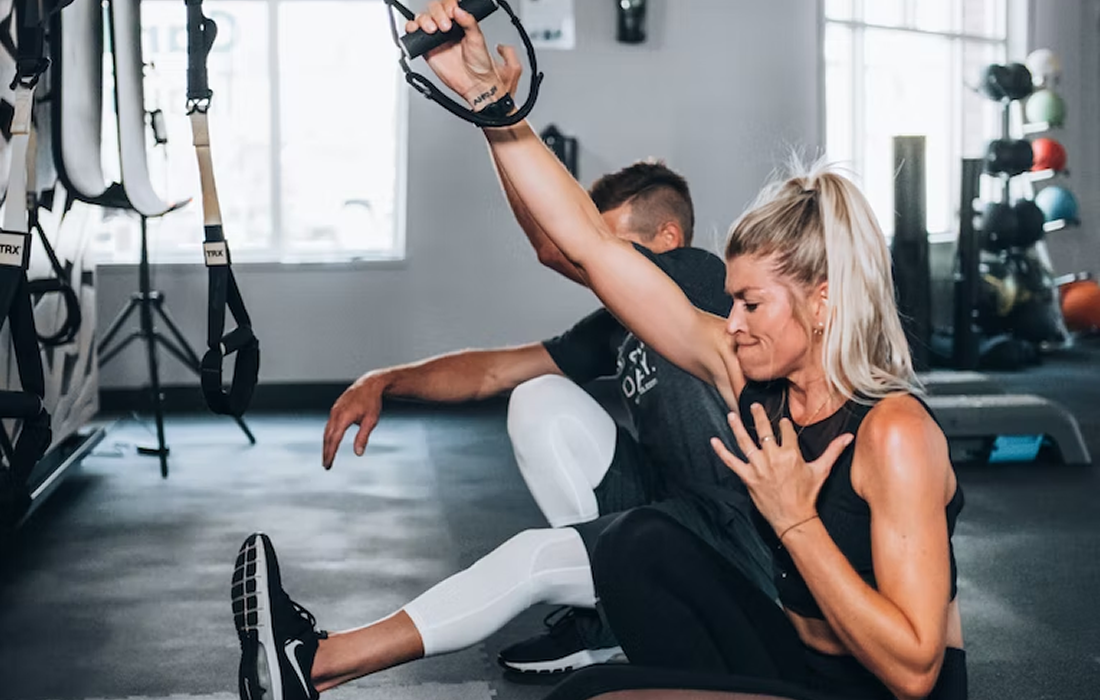
It is well documented that regular physical activity is associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and premature death. In 2018, the United States Department of Health and Human Services’ Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommended that adults engage in at least 150-300 minutes/week of moderate physical activity or 75-150 minutes/week of vigorous physical activity, […]
The outer layer of skin, the epidermis, is constantly turning over to replace dead or damaged cells throughout our lifetime. Skin stem cells need to continuously make decisions: either make more copies of themselves (self-renewal) or switch their fate towards differentiation. The gene regulatory mechanisms governing these two distinct progenitor fate choices, especially the early […]
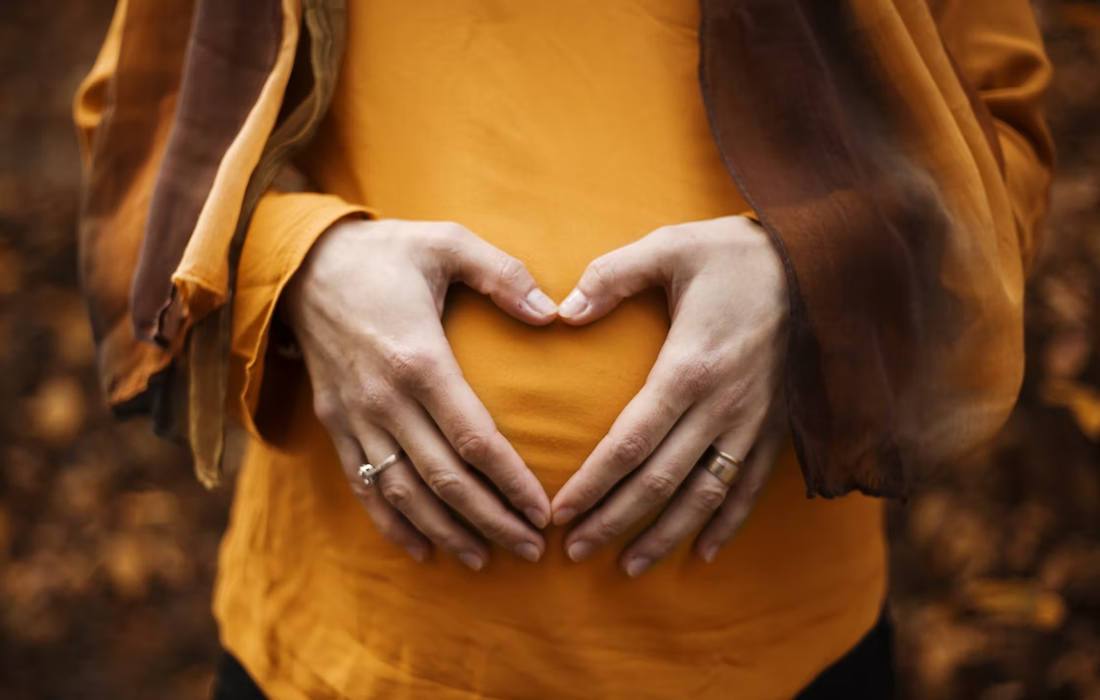
Menopause is the permanent cessation of menstruation resulting in the loss of ovarian follicle development. It is considered to occur when 12 menstrual cycles are missed, and typically signals the end of a woman’s ability to become pregnant. Early menopause, iis described as the cessation of ovarian function at or before the age of […]
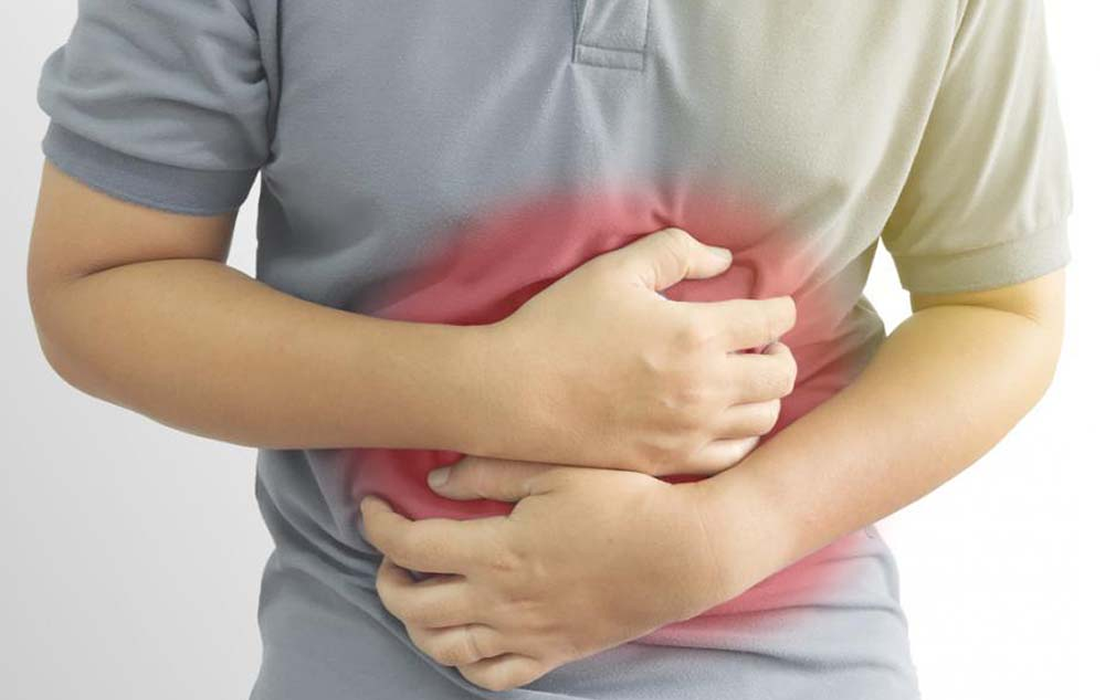
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal (GI) disorder characterized by abdominal pain and altered bowel habit in the absence of a specific and unique organic pathology, although microscopic inflammation has been documented in some patients. Population-based studies estimate the prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome at 10-20% and the incidence of irritable bowel syndrome […]
After muscle injury, muscle stem cells must coordinate with immune cells in the inflamed tissue to ensure efficient repair. In damaged muscle, stem cells must work together with immune cells to complete the repair process, yet how these cells coordinate to ensure the efficient removal of dead tissue before making new muscle fibers has remained […]
Depression affects 264 million persons in the world, accounting for some 4.3% of the global burden of disease. Major depressive disorder has significant potential morbidity and mortality, contributing to suicide, incidence and adverse outcomes of medical illness, disruption in interpersonal relationships, substance abuse, and lost work time. During 2009–2012, 7.6% of Americans aged 12 and […]
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD) is the most common cause of irreversible vision loss in the developed world. AMD is associated with the presence of drusen, without visual loss early in the disease. However, the disease often slowly progresses over years to retinal atrophy and central retinal degeneration with associated loss of central vision. […]
Vitamin D is a pro-hormone and an essential micronutrient, and although its classical roles are related to the regulation of calcium homeostasis, various types of immune cells express both the vitamin D receptor and metabolizing enzymes, suggesting that hormonal vitamin D could also play a role in modulating inflammatory responses. This is supported by an […]